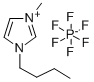
174501-64-5
- Product Name:1H-Imidazolium, 3-butyl-1-methyl-, hexafluorophosphate(1-) (1:1)
- Molecular Formula:C8H15N2.PF6
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 174501-64-5
Molecular Formula: C8H15N2.PF6
Appearance: Clear pale yellow oil
174501-64-5 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C8H15N2.PF6
- Molecular Weight:284.185
- Appearance/Colour:Clear pale yellow oil
- Melting Point:6.5 °C
- Refractive Index:n20/D 1.41
- Boiling Point:>340°C
- Flash Point:>350°C
- PSA:22.40000
- Density:1.38 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.)
- LogP:4.49510
174501-64-5 Usage
Conductivity
1.92 mS/cm
Chemical Properties
Clear pale yellow oil
Uses
those consisting of tetrafluoroborate, alkylsulfate, alkylsulfonate, carboxylate, or phosphate anions are hydrophilic and are completely dissolved in water. Dupont and coworkers first reported stable hydrophobic imidazolium salt, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C4mim][PF6]) in 1996. Since then, this salt has been used as a typical hydrophobic IL in many chemical reactions because its mixture with water forms a biphasic layer. Furthermore, this IL shows poor solubility in hexane or ether, which allows realization of an easy work-up process. However, [C4mim][PF6] was reported to be sensitive to the moisture at high temperature and produced hazardous hydrogen fluoride as it decomposed. Therefore, bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide (NTf2) salts are now recommended as the anion for preparing hydrophobic ILs.
Uses
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate is an ionic liquid employed in many environmentally friendly reactions. It can also be used as a medium for reactions such as: Ring-closing metathesis of diene and enyne substrates in the presence of a novel recyclable ruthenium carbene complex.Nickel(II)acetylacetonate catalyzed oxidation of aromatic aldehydes to the corresponding acids using dioxygen as the oxidant.Lipase-catalyzed enantioselective acylation of allylic alcohols.Allylation of aldehydes using tetraallylstannane to yield homoallylic alcohols.
General Description
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate is an imidazolium-based, hydrophobic, room temperature ionic liquid (RTIL). It can be prepared by reacting 1-methylimidazole with chlorobutane. Gaseous hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) such as fluoromethane, fluoroethane and 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane are soluble in BMIMPF6.
InChI:InChI=1/C8H16N2.F6P/c1-3-4-5-10-7-6-9(2)8-10;1-7(2,3,4,5)6/h6-7H,3-5,8H2,1-2H3;/q;-1/p+1
174501-64-5 Relevant articles
High performance asymmetric supercapacitor based on MnO2 electrode in ionic liquid electrolyte
Zhang, Xuan,Zhao, Dandan,Zhao, Yongqing,Tang, Pengyi,Shen, Yinglin,Xu, Cailing,Li, Hulin,Xiao, Yu
, p. 3706 - 3712 (2013)
In this work, the electrochemical properties of a MnO2 nanocomposite electrode were investigated in 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([Bmim]PF6)/N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) electrolyte. The [Bmim]PF6/DMF electrolyte with different volume fractions exhibits significant influence on the electrochemical properties of the electrode. When the volume ratio of [Bmim]PF6 and DMF was 1:1, the electrode showed the best electrochemical performance. The operation potential window of the MnO2 nanocomposite electrode in ionic liquids was 2.1 V and the specific capacitance according to the mass of MnO2 was 523.3 F g-1 at 3 A g-1. Then, a high-voltage (3 V) MnO2 asymmetric supercapacitor was successfully fabricated, using the MnO2 nanocomposite electrode, activated carbon and [Bmim]PF 6/DMF as the positive electrode, negative electrode and electrolyte, respectively. The MnO2 asymmetric supercapacitor displayed a maximum specific energy of 67.5 W h kg-1 at a specific power of 593.8 W kg-1 and a maximum specific power of 20.4 kW kg-1 at a specific energy of 8.5 W h kg-1. The impressive results showed that [Bmim]PF6/DMF could be a promising electrolyte for MnO2 supercapacitors.
Examination of ionic liquids and their interaction with molecules, when used as stationary phases in gas chromatography
Armstrong, Daniel W.,He, Lingfeng,Liu, Yan-Song
, p. 3873 - 3876 (1999)
Stable room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) have been used as novel reaction solvents. They can solubilize complex polar molecules such as cyclodextrins and glycopeptides. Their wetting ability and viscosity allow them to be coated onto fused silica capillaries. Thus, 1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate and the analogous chloride salt can be used as stationary phases for gas chromatography (GC). Using inverse GC, one can examine the nature of these ionic liquids via their interactions with a variety of compounds. The Rohrschneider-McReynolds constants were determined for both ionic liquids and a popular commercial polysiloxane stationary phase. Ionic liquid stationary phases seem to have a dual nature. They appear to act as a low-polarity stationary phase to nonpolar compounds. However, molecules with strong proton donor groups, in particular, are tenaciously retained. The nature of the anion can have a significant effect on both the solubilizing ability and the selectivity of ionic liquid stationary phases. It appears that the unusual properties of ionic liquids could make them beneficial in many areas of separation science.
One-pot and solventless synthesis of ionic liquids under ultrasonic irradiation
Estager, Julien,Lévêque, Jean-Marc,Cravotto, Giancarlo,Boffa, Luisa,Bonrath, Werner,Draye, Micheline
, p. 2065 - 2068 (2007)
A novel method is described for the one-pot synthesis of various ionic liquids in a competitive time. By using ultrasonic irradiation, different families of nitrogen-bearing ionic liquids can be obtained in a solvent-free or in aqueous medium, which gives a greener touch to the overall process. Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart.
Association of ionic liquids in solution: Conductivity studies of [BMIM][Cl] and [BMIM][PF6] in binary mixtures of acetonitrile + methanol: Ion association in ionic liquid solutions
Jan, Roohi,Rather, Ghulam Mohammad,Bhat, Mohsin Ahmad
, p. 738 - 745 (2013)
The concentration dependence of molar conductance for 1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium chloride and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate in binary mixtures of acetonitrile + methanol was investigated to explore the ion association behavior of imidazolium based ionic liquids. The limiting molar conductance (Λm0), association constants (K a 0) and the maximal distance between the oppositely charged ions in ion pairs (R ij ) in the mixed solvent mixtures were evaluated following the framework of Barthel's low-concentration chemical model. The investigated ILs display opposing trends in ion association behavior with change in solvent composition of acetonitrile + methanol binary mixtures. The results are discussed in light of ionic liquid and solvent specific ion-solvent and ion-ion interactions in the mixed solvent systems.
Effect of temperature on the purity of product in the preparation of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids
K?rkk?inen, Johanna,Asikkala, Janne,Laitinen, Risto S.,Lajunen, Marja K.
, p. 763 - 770 (2004)
The preparation of room-temperature ionic liquids 1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium chloride, hexafluorophosphate, and dicyanamide by microwave-assisted reaction in non-solvent and solvent conditions has been studied in this contribution. A special emphasis is put on the effect of the reaction temperature on the purity of ionic liquids that was monitored by electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry and 1H NMR. The X-ray structure of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride is presented.
Liquid-liquid equilibria of room-temperature ionic liquids and butan-1-ol
Wu,Marsh, Kenneth N.,Deev, Alexander V.,Boxall, John A.
, p. 486 - 491 (2003)
Room-temperature ionic liquids are salts that are liquid at room temperature. Their use as catalysts and catalytic support has been studied extensively. However, there are very few measurements on their solubility and phase equilibria in common organic solvents. In this work, the liquid-liquid phase equilibria of mixtures of room-temperature ionic liquids, 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, [Rnmim][PF6] (1) where Rn = butyl, pentyl, hexyl, heptyl, and octyl, with butan-1-ol (2) over a composition range have been measured. The binodal coexistence curves of the mixtures were found to have an upper critical solution temperature (USCT) at x2 ≈ 0.9. The UCST decreases with increase in the length of the alkyl chain of the ionic liquid, with the UCST of the butyl at 373 K and that of the octyl at 326 K. Both the UCST and the composition at the UCST as a function of the 1-alkyl group chain length can be reasonably well predicted from theory on the basis of unimolecular quantum chemical calculations.
Spectroscopic and photophysical properties of ZnTPP in a room temperature ionic liquid
Szmytkowski, Jedrzej,Bond, Toby,Paige, Matthew F.,Scott, Robert W. J.,Steer, Ronald P.
, p. 11471 - 11476 (2010)
The steady-state absorption and emission spectra and the time-resolved Soret- and Q-band excited fluorescence profiles of the model metalloporphyrin, ZnTPP, have been measured in a highly purified sample of the common room temperature ionic liquid, [bmim][PF6]. S2-S0 emission resulting from Soret-band excitation behaves in a manner completely consistent with that of molecular solvents of the same polarizability. The ionic nature of the solvent and its slow solvation relaxation times have no significant effect on the nature of the radiationless decay of the S2 state, which decays quantitatively to S1 at a population decay rate that is consistent with the weak coupling case of radiationless transition theory (energy gap law). The ratio of the intensities of the Qα:Qβ (0-0:1-0) bands is consistent with the solvatochromic shift correlation data obtained for molecular solvents. The temporal S1 fluorescence decay profiles measured at a single emission wavelength are biexponential; the longer-lived major component is similar to that observed for ZnTPP in molecular solvents, and the minor shorter-lived component is attributed to solvent relaxation processes on a nanosecond time scale.
A rationalization of the solvent effect on the Diels-Alder reaction in ionic liquids using multiparameter linear solvation energy relationships
Bini, Riccardo,Chiappe, Cinzia,Mestre, Veronica Llopsis,Pomelli, Christian Silvio,Welton, Thomas
, p. 2522 - 2529 (2008)
The Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and three dienophiles (acrolein, methyl acrylate and acrylonitrile) having different hydrogen bond acceptor abilities has been carried out in several ionic liquids and molecular solvents in order to obtain information about the factors affecting reactivity and selectivity. The solvent effects on these reactions are examined using multiparameter linear solvation energy relationships. The collected data provide evidence that the solvent effects are a function of both the solvent and the solute. For a solvent effect to be seen, the solute must have a complimentary character; selectivities and rates are determined by the solvent hydrogen bond donation ability (α) in the reactions of acrolein and methyl acrylate, but not of acrylonitrile. The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008.
Preparation of second generation ionic liquids by efficient solvent-free alkylation of N-heterocycles with chloroalkanes
Cravotto, Giancarlo,Gaudino, Emanuela Calcio,Boffa, Luisa,Leveque, Jean-Marc,Estager, Julien,Bonrath, Werner
, p. 149 - 156 (2008)
Non-conventional techniques, such as microwave (MW) and power ultrasound (US) as well as combined MW/US irradiation, have been used to promote one-pot synthesis of second-generation ionic liquids (ILs), cutting down reaction times and improving yields. However, the use of chloroalkanes in the alkylation of N-heterocycles requires more drastic conditions if results are to match those obtained with more reactive alkyl halides. The present paper describes a series of MW- or MW/US-promoted IL preparations starting from chloroalkanes and classic heterocycles (1-methylimidazole, pyridine and 1-methylpyrrolidine). When reactions were carried out under conventional heating in an oil bath they required longer reaction times and gave poorer yields. 1H-NMR analysis and ion-exchange chromatography showed that the present solventless procedure afforded ILs of satisfactory purity. The observed high yields (usually 70-98% isolated), and short reaction times showed that a straightforward access to ILs can be also achieved with the use of alkyl chlorides, resulting in a considerable reduction of costs.
Effect of ionic liquids on the conformation of a porphyrin-based viscometer
Jameson, Laramie P.,Kimball, Joseph D.,Gryczynski, Zygmunt,Balaz, Milan,Dzyuba, Sergei V.
, p. 18300 - 18304 (2013)
Structure of the cationic and anionic counterparts of ionic liquids has a significant impact on the conformational bias of the porphyrin rotor; an apparent correlation between the conformation and the viscosity of ionic liquids was noted, albeit it was found to be distinct and more complex from that found in molecular solvents.
Anthralin: Primary products of its redox reactions
Czerwinska, Malgorzata,Sikora, Adam,Szajerski, Piotr,Zielonka, Jacek,Adamus, Jan,Marcinek, Andrzej,Piech, Krzysztof,Bednarek, Pawel,Bally, Thomas
, p. 5312 - 5319 (2006)
One-electron reduction significantly enhances the ability of anthralin, 1, to act as a hydrogen atom donor. On annealing of an MTHF glass in which the radical anion of anthralin, 1.-, is generated radiolytically, this species decays mainly by loss of H. to give the anthralyl anion, 2. On the other hand, radicals formed on radiolysis of matrices that are suitable for the generation of radical anions or cations are capable to abstract H . from anthralin to give the anthralyl radical, 2.. Both 2- and 2. are obtained simultaneously by mesolytic cleavage of the radical anion of the anthralin dimer. Contrary to general assumptions, the anthralyl radical is found to be much more reactive toward oxygen than the anion. All intermediates are characterized spectroscopically and by reference to quantum chemical calculations. Attempts to generate the radical cation of anthralin by X-irradiation of an Ar matrix containing anthralin led also to significant formation of its radical anion, i.e., anthralin acts apparently as an efficient electron trap in such experiments.
Capillary electrophoretic application of 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids
Yanes,Gratz,Baldwin,Robison,Stalcup
, p. 3838 - 3844 (2001)
Ionic substances with melting points at or close to room temperature are referred to as ionic liquids. Interest in ionic liquids for their potential in different chemical processes is increasing, because they are environmentally benign and are good solvents for a wide range of both organic and inorganic materials. In this study, a capillary electrophoretic method for resolving phenolic compounds found in grape seed extracts is reported. The method, in which 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids are used as the running electrolytes, is simple and reproducible. The separation mechanism seems to involve association between the imidazolium cations and the polyphenols. The role of the alkyl substituents on the imidazolium cations was investigated and will be discussed.
Physicochemical properties and structures of room temperature ionic liquids. 1. Variation of anionic species
Tokuda, Hiroyuki,Hayamizu, Kikuko,Ishii, Kunikazu,Susan, Md. Abu Bin Hasan,Watanabe, Masayoshi
, p. 16593 - 16600 (2004)
Room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) based on 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium ([bmim]) with a variety of fluorinated anions were prepared, and the thermal behavior, density, viscosity, self-diffusion coefficients of the cations and anions, and ionic conductivity were measured over a wide temperature range. The temperature dependencies of the self-diffusion coefficient, viscosity, ionic conductivity, and molar conductivity have been fitted to the Vogel-Fulcher-Tamman equation, and the best-fit parameters for the self-diffusion coefficient, viscosity, ionic conductivity, and molar conductivity have been estimated, together with the linear fitting parameters for the density. The self-diffusion coefficients determined for the individual ions by pulsed-field-gradient spin-echo NMR method exhibit higher values for the cation compared with the anion over a wide temperature range, even if its radius is larger than that of the anionic radii. The summation of the cationic and anionic diffusion coefficients for the RTILs follows the order [bmim][(CF3SO2N] > [bmim][CF 3CO2] > [bmim][CF3SO3] > [bmim][BF4] > [bmim][(C2F5SO 2)2N] > [bmim][PF6] at 30?°C, and the order of the diffusion coefficients greatly contrasts to the viscosity data. The ionic association is proposed from the results of the ratios of molar conductivity obtained from impedance measurements to that calculated by the ionic diffusivity using the Nernst-Einstein equation. The ratio for the ionic liquids follows the order [bmim][PF6] > [bmim][BF4] > [bmim][(C2F5SO2)2N] > [bmim][(CF3SO2)2N] > [bmim][CF 3SO3] > [bmim][CF3CO2] at 30?°C and provides quantitative information on the active ions contributing to ionic conduction in the diffusion components.
Thermal phase behavior of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate: Simultaneous measurements of the melting of two polymorphic crystals by Raman spectroscopy and calorimetry
Endo, Takatsugu,Nishikawa, Keiko
, p. 79 - 82 (2013)
The thermal phase behavior of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, which forms three polymorphic crystals (α, β, and γ), has been re-investigated by the simultaneous measurements of Raman spectroscopy and calorimetry. The peak assigned to the phase change from β to γ phase is found to be exothermic and, in striking contrast with a previous report, the peak for this transition is observed near 255 K by recooling and subsequent reheating of the β phase. This finding enabled separate measurements of the melting points (285.8 and 285.3 K), fusion enthalpies (13.1 and 22.6 kJ mol-1), and entropies of the β and γ phases, respectively.
Liquid-Crystalline Ionic Liquids as Ordered Reaction Media for the Diels–Alder Reaction
Bruce, Duncan W.,Gao, Yanan,Canongia Lopes, José Nuno,Shimizu, Karina,Slattery, John M.
, p. 16113 - 16123 (2016)
Liquid-crystalline ionic liquids (LCILs) are ordered materials that have untapped potential to be used as reaction media for synthetic chemistry. This paper investigates the potential for the ordered structures of LCILs to influence the stereochemical outcome of the Diels–Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and methyl acrylate. The ratio of endo- to exo-product from this reaction was monitored for a range of ionic liquids (ILs) and LCILs. Comparison of the endo:exo ratios in these reactions as a function of cation, anion and liquid crystallinity of the reaction media, allowed for the effects of liquid crystallinity to be distinguished from anion effects or cation alkyl chain length effects. These data strongly suggest that the proportion of exo-product increases as the reaction media is changed from an isotropic IL to a LCIL. A detailed molecular dynamics (MD) study suggests that this effect is related to different hydrogen bonding interactions between the reaction media and the exo- and endo-transition states in solvents with layered, smectic ordering compared to those that are isotropic.
18-crown-6 and dibenzo-18-crown-6 assisted extraction of cesium from water into room temperature ionic liquids and its correlation with stability constants for cesium complexes
Vendilo, Andrey G.,Djigailo, Dmitry I.,Smirnova, Svetlana V.,Torocheshnikova, Irina I.,Popov, Konstantin I.,Krasovsky, Vladimir G.,Pletnev, Igor V.
, p. 5001 - 5016 (2009)
The pH-profiles of the extraction of Cs+ into four conventional (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate and bis[trifluoromethyl) sulphonyl]imides of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium, and 1-(2-ethylhexyl)-3-methylimidazolium) and two novel (trioctylmethylammonium salicylate and tetrahexyl-ammonium dihexylsulfosuccinate) room temperature ionic liquids have been determined both in the absence and in the presence of crown ether (18-crown-6 or dibenzo-18-crown-6). The pH-profiles of distribution ratio of crown ethers have been established in the same conditions. The relationship of cesium extraction efficiency both with the stability of its complexes with crown ethers and crown ethers' distribution ratio has been clarified.
Controlling the reactions of 1-bromogalactose acetate in methanol using ionic liquids as co-solvents
Gilbert, Alyssa,Haines, Ronald S.,Harper, Jason B.
, p. 5442 - 5452 (2020)
The reactions of an acetobromogalactose in mixtures of methanol and one of seven different ionic liquids with varying constituent ions were studied. In general, small amounts of ionic liquid in the reaction mixture led to increases in the rate constant compared to methanol, whilst large amounts of ionic liquid led to decreases in the rate constant; this outcome differs significantly from previous reactions proceeding through this mechansim. Temperature dependent kinetic studies indicated that the dominant interaction driving these changes was between the ionic liquid and the transition state of the process. Through considering solvent parameters of ionic liquids, a relationship was found between the changes in the rate constant and both the hydrogen bond accepting ability and polarisability of the solvent, indicating that the interactions affecting reaction outcome are both specific and non-specific in nature; once more, these interactions were different to those observed in previous similar reactions. By changing the amount of ionic liquid in the reaction mixture, additional products not seen in the molecular solvent case were observed, the ratios of which are dependent on the anion of the ionic liquid and the proportion of ionic liquid in the reaction mixture. This demonstrates the importance of considering solvent effects on both the rate and product determining steps and the potential application of such changes is discussed.
Understanding the effects of ionic liquids on a unimolecular substitution process: Correlating solvent parameters with reaction outcome
Gilbert, Alyssa,Haines, Ronald S.,Harper, Jason B.
, p. 675 - 682 (2019)
A unimolecular substitution process was studied in five different ionic liquids, with systematic variation of either the cation or anion, in order to determine the factors leading to the increase in the rate constant for the process relative to acetonitrile. It was found that both components of the ionic liquid, and the proportion of the salt in the reaction mixture, affect the rate constant. Activation parameters determined for the process suggest that there is a balance between interactions of the components of the ionic liquid with both starting material and transition state. A correlation was found between the rate constant and a combination of Kamlet-Taft solvent parameters; with the polarisability of the solvent being the most significant factor. As this reaction proceeds through both unimolecular and bimolecular pathways, competition experiments determined that the unimolecular pathway for the reaction can be favoured using small amounts of ionic liquid in the reaction mixture, demonstrating the potential to control reaction mechanisms using ionic liquids.
A general and direct synthesis of imidazolium ionic liquids using orthoesters
Kim, Do Joong,Oh, Kyung Hwan,Park, Jin Kyoon
, p. 4098 - 4101 (2014)
A general method to synthesize halide and halide-free ionic liquids was developed. Direct alkylation of imidazole and pyridine derivatives was performed in the presence of an acid using an orthoester as the alkyl donor yielding ionic liquid products. Residual Cl and water contents of the ionic liquids were determined by ion chromatography and a Karl-Fisher test. the Partner Organisations 2014.
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of Imidazolium-Based Zwitterions: The Intramolecular Charge-Transfer Effect
Shuang Men,Yujuan Jin
, p. 2337 - 2340 (2018)
Abstract: We investigate the imidazolium-based zwitterions, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium-2-pentafluorophosphate, together with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The intramolecular charge-transfer from the negative headgroup to the positive headgroup is revealed in detail. In the case of the zwitterions, due to the intense charge-transfer effect, binding energies of N 1s and C2 1s are both lower; whilst P 2p is higher, compared to those of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Such effect is found negligible for F 1s spectra. It is found that F 1s binding energies for the two samples are the same.
How to predict the physical properties of ionic liquids: A volume-based approach
Slattery, John M.,Daguenet, Corinne,Dyson, Paul J.,Schubert, Thomas J. S.,Krossing, Ingo
, p. 5384 - 5388 (2007)
(Chemical Equation Presented) The molecular volume Vm (that is, the sum of the ionic volumes Vion of the constituent ions) of an ionic liquid (IL) in combination with an anion-dependent empirical relationship is all one needs to predict physical properties such as viscosity, conductivity, and density of [N(CN)2]-, [BF4]-, [PF6]-, and [N(SO2CF3) 2]- ionic liquids, including those which may as yet only exist on paper.
Modelling catalytic turnover frequencies in ionic liquids: The determination of the bimolecular rate constant for solvent displacement from [(C6H6)Cr(CO)2Solv] in 1-w-butyl-3- methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
Swiderski, Konrad,McLean, Andrew,Gordon, Charles M.,Vaughan
, p. 590 - 591 (2004)
The bimolecular rate constant for solvent displacement, k2, from [(C6H6)Cr(CO)2Solv] by an incoming ligand has been determined in the room temperature ionic liquid, [bmim][PF 6], and is compared to that for the same process in cyclohexane and dichloroethane.
Ionic Liquids: Additives for Manipulating the Nucleophilicity
Rather, Mudasir Ahmad,Rather, Ghulam Mohammad,Pandit, Sarwar Ahmad,Bhat, Sajad Ahmad,Khan, Khaliquz Zaman,Bhat, Mohsin Ahmad
, p. 1518 - 1528 (2015)
Kinetic investigations of the SN2 reaction at the sulfur atom of p-toluenesulfonyl chloride with sodium azide in dried methanol in the presence of varying amounts of room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs), 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ([C4C1im][CH3COO]), 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([C4C1im]Cl) and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C4C1im][PF6]), were carried out in order to explore and understand the impact of these additives on the rate of such reactions. The observed results indicate that the rate constant of the reaction increase appreciably with increases in the concentration of RTILs in RTIL-methanol binary solvent systems. The results were analyzed in light of a Kamlet-Taft model system, which established that the observed impact of RTILs can be attributed to the cumulative effects of increase in the β value (hydrogen bonding acceptor ability) which is expected to enhance the reactivity of p-toluenesulfonyl chloride as well as the nucleophilicity of the azide ion and decrease in the πvalue (solvent dipolarity/polarizability) which is expected to enhance the reactivity of the azide ion. Of the three ionic liquids used in the presented studies, [C4C1im][CH3COO] was observed to be more effective in accelerating the rate constant; this we attribute to its comparatively stronger ability to increase the β value and decrease the πvalue in the mixed solvent system.
A Novel and Eco-friendly Method for the Preparation of Ionic Liquids
Xu, Dan-Qian,Liu, Bao-You,Luo, Shu-Ping,Xu, Zhen-Yuan,Shen, Yin-Chu
, p. 2626 - 2628 (2003)
A novel and eco-friendly method is described for the direct preparation of a series of ionic liquids containing alkylimidazolium-based cations and hexafluorophosphate-based (or tetrafluoroborate-based) anions in a one-pot procedure by using ionic liquids themselves as solvents.
Introduction of an ordered porous polymer network into a ceramic alumina membrane via non-hydrolytic sol-gel methodology for targeted dynamic separation
Meng, Minjia,Liu, Yan,Zhang, Min,Feng, Yonghai,Yan, Yongsheng
, p. 38630 - 38642 (2014)
A highly selective composite imprinted alumina membrane (CIAM) for gentisic acid (GA) was successfully synthesized by the nonhydrolytic sol-gel (NHSG) method with room temperature ionic liquid (RTIL) as the pore template. The carboxylic acid was used as both the functional monomer and the catalyst to form the alumina membrane-based porous imprinted polymer layer. The adsorption capacities, fluxes and permeation selectivities of various CIAMs suggested that cinnamic acid (CA) was the promising functional monomer for preparing a CIAM to separate GA from salicylic acid (SA) and the incorporation of RTIL improved the selectivity of GA over CIAM. The amount of porous imprinted polymer layer on the CIAM significantly affected the separation of GA from SA over CIAM. A three-level Box-Behnken experimental design with three factors combining the response surface modeling was used to optimize the dynamic separation process. The experimental data were well fitted to a second-order polynomial equation using multiple regression analysis. The optimal conditions for the separation of GA from SA were as follows: GA concentration of 0.0325 mmol L-1, temperature of 15.0 °C and flow rate of 1.0 mL min-1. Under these conditions, the experimental separation factor was 13.26 ± 0.87%, which was close to the predicted separation factor. the Partner Organisations 2014.
A hybrid electrochemical-colorimetric sensing platform for detection of explosives
Forzani, Erica S.,Lu, Donglai,Leright, Matthew J.,Aguilar, Alvaro Diaz,Tsow, Francis,Lalesias, Rodriao A.,Lu, Jin,Tao, Nongjian,Zhang, Qian,Li, Jinghong
, p. 1390 - 1391 (2009)
-
Separation/preconcentration of trace copper by extraction into [C 4mim] [PF6] RITL containing p-tert-butyl-calix[4]arene functionalized with o-phenanthroline prior to flame absorption atomic spectrometry
Ma, Lina,Zhu, Xiashi,Wang, Wenjun
, p. 20 - 24 (2013)
A liquid-liquid extraction (LLE)-flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) for the separation/analysis of copper has been developed. The method was based on the fact that the inclusion complex of copper(II) with 25, 27-di (5-phenanthrolinylaminocarbonylmethoxy)-26,28-dihydroxy-p-tert-butylcalix[4] arene (TBCP) could be extracted into room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluoro-phosphate [C4mim] [PF 6] as the green extractant, TBCP as the complexlant), and the copper(II) was subsequently determined by FAAS. The LLE was optimized in detail. The selectivity and mechanism of LLE were approached. Under optimized experimental conditions, the linear range of calibration curve for the determination of copper(II) was 0.020-10.0 μg/mL. The detection limit estimated (S/N = 3) was 3.59 ng/mL with 3.0% RSD. It has been applied for the determination of copper(II) in water samples with satisfactory results.
A speedy one-pot synthesis of second-generation ionic liquids under ultrasound and/or microwave irradiation
Cravotto, Giancarlo,Boffa, Luisa,L'Eveque, Jean-Marc,Estager, Julien,Draye, Micheline,Bonrath, Werner
, p. 946 - 950 (2007)
The present work describes an efficient one-pot synthesis of second-generation ionic liquids (ILs), combining in one step the Menshutkin reaction and anion metathesis. Working in a closed vessel under microwaves, or better still under simultaneous ultrasound and/or microwave irradiation, in a few minutes a series of ILs with 1-methylimidazole or pyridine cores were obtained in high yields (80?97% isolated). Under conventional heating, ILs could not be prepared in one pot in acceptable times and yields, whereas our protocol, carried out with commercially available equipment, was highly effective and reproducible. Moreover, 1H NMR analysis and ion-exchange chromatography showed that the present solventless procedure afforded satisfyingly pure ILs. CSIRO 2007.
Impregnation of different ionic liquids onto cationic starch and their comparison in the extraction of Th(IV)
Bursali, Elif Ant,Bozkurt, Serap Seyhan,Yurdako?, Mürüvvet
, p. 364 - 372 (2016)
Cationic starch (CS) was prepared by using epichlorohydrin (EPI) and 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride (CHPTMA) and ionic liquids (ILs) having different anionic groups [1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate (BMI+ BF-4), ),lyhtem-3-lytub-1imidazolium (BMIIMB(+ Br Br-), 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium hexafluorophosphate (BMI+ PF-6 ), and 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium bis-[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide (BMI+ [(TF)2 N]-)] were impregnated onto CS. Thorium(IV) ions were preconcentrated by using IL impregnated CS. The effects of ILs were investigated for extraction of Th(IV) by CS and the results were compared. Th(IV) was preconcentrated with approximately 73% sorption capacity by CS and increased up to 98%-100% for IL impregnated sorbents at pH 7.0. The sorption capacities of Th(IV) were 0.453 mmol g-1 , 0.399 mmol g-1 , 0.281 mmol g-1 , and 0.183 mmol g-1 CS-BMI+ Br- , CS-BMI+ [(TF)2 N], CS-BMI+ PF-6 andCS-BMI+ BF-4 , respectively. The elution occurred with HCl and NaOH solutions at pH 7.0. for.
Solvatochromic probe behavior within ternary room-temperature ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate + ethanol + water solutions
Fletcher, Kristin A.,Pandey, Siddharth
, p. 13532 - 13539 (2003)
The solvatochromic probe behavior within ternary BMIMPF6 + ethanol + water systems were investigated using four solvatochromic probes: pyrene, 1,3-bis(1-pyrenyl)propane, 1-pyrenecarboxaldehyde, and Reichardt's betaine dye (BMIMPF6 [1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate] is one of the most popular room-temperature ionic liquids [RTIL]). A simplified preferential solvation model based on the weighted mole fraction probe response shows that the pyrene cybotactic region is rich in BMIMPF6 compared to the bulk. However, the 1,3-bis(1-pyrenyl)propane and 1-pyrenecarboxaldehyde solvation environments appear to be ethanol enriched. Although the aldehyde functional moiety on 1-pyrenecarboxaldehyde may explain an ethanol-rich cybotactic region, a significant decrease in bulk viscosity (more than that predicted from additivity) of BMIMPF6 upon aqueous-ethanol addition may result in an increased intramolecular excimer formation efficiency of 1,3-bis(1-pyrenyl)propane. ET(30) values in ternary BMIMPF6 + ethanol + water solutions are higher than those observed in neat BMIMPF6 or aqueous ethanol, suggesting a local solvation environment rich in water. The results strongly suggest that the physicochemical properties of this RTIL can be modulated in a controlled fashion by adding appropriate amounts of aqueous ethanol.
Do anions influence the polarity of protic ionic liquids?
Shukla, Shashi Kant,Khupse, Nageshwar D.,Kumar, Anil
, p. 2754 - 2761 (2012)
Polarity studies in two classes of imidazolium-based protic ionic liquids (PILs) possessing [HSO4]-, [HCOO]-, [CH 3COO]- and [CH3CH2COO]- anions were carried out using a solvatochromic method from 298.15 to 353.15 K. For 1-methylimidazolium class of PILs, ET(30) was found to be independent over the entire range of temperature, while ET(30) was noted to decrease with a rise in temperature in the case of 1-butylimidazolium class of PILs containing [CH3COO]- and [CH 3CH2COO]- anions. The ET(30) value decreases in both the classes upon varying the anions ([HSO4] -, [HCOO]-, [CH3COO]- and [CH 3CH2COO]-). The ET(30) value is controlled by hydrogen bond acceptor basicity, β, and dipolarity/ polarizability, π*. The ET(30) value for PILs varies inversely to the strength of the coulombic interaction between ions in PILs. Strong interactions between ions lead to lower ET(30) values. Unlike the poor thermal effect on ET(30), the Kamlet-Taft parameters i.e. α, β and π* have pronounced thermal effect in the imidazolium-based PILs. Variation in the Kamlet-Taft parameters is controlled by the stabilization of ions and the degree of proton transfer from Bronsted acid to Bronsted base. the Owner Societies 2012.
Exploring physicochemical aspects of N-alkylimidazolium based ionic liquids
Bhat, Mohsin Ahmad,Dutta, Chanmeet K.,Rather, Ghulam Mohammad
, p. 142 - 151 (2013)
Physicochemical aspects (structural, thermodynamic and transport) of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([BMIM][BF4]), 1-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([BDMIM][BF4]) and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([BMIM][PF6]) room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) are reported. The results based on temperature dependence of surface tension, conductivity, photoluminescence and spectroscopic measurements on RTILs and their mixtures with acetonitrile (ACN) as cosolvent are interpreted in-terms of structure-composition-property relations. The presented observations clearly indicate that a highly structured and organized arrangement of constituents prevails in the investigated RTILs, which is sensitive to temperature variations and cosolvent addition. Thermodynamic and structural parameters estimated from temperature dependency of interfacial tension demonstrate that surface characteristics are dominated by covalent interactions in imidazolium based RTILs. From composition dependence of measured parameters in RTIL-cosolvent mixtures it is shown that ACN mixes nonideally with RTIL, and interestingly the investigated RTILs retain their inherent structural order up to high dilution limits (0.3 volume fraction of RTIL), beyond which these behave as associated electrolytes. The presented findings seem useful for arriving at molecular basis of physicochemical aspects and future applications of RTILs and their binary mixtures especially with cosolvents for biphasic catalysis and heterogeneous electron transfer reactions, wherein temperature elevation and cosolvent addition are currently advocated as operationally simple means to speed up the mass transport.
Simultaneous determination of Brilliant Green and Crystal Violet dyes in fish and water samples with dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction using ionic liquid followed by zero crossing first derivative spectrophotometric analysis method
Sadeghi, Susan,Nasehi, Zohreh
, p. 134 - 142 (2018)
In this study, dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction using ionic liquid (IL-DLLME) combined with zero crossing first derivative spectrophotometric method was applied to quantitative determination of triphenylmethane dyes in binary mixtures. The 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [OMIM][PF6] ionic liquid was used to extract Brilliant Green (BG) and Crystal Violet(CV) dyes from aqueous solutions. The amplitude of the zero crossing first derivative spectra at 670 nm and 532 nm were selected for the determination of BG and CV, respectively. Significant factors influencing the extraction of BG and CV such as sample pH, kind of extraction solvent, amount of extractant, extraction and centrifuging times and ionic strength were investigated. Under the optimal conditions, the calibration curves for the simultaneous determination of both dyes were found to be linear in the range of 10–500 μg L?1 with detection limits (LODs) of 2.7 μg L?1 and 1.4 μg L?1 for BG and CV, respectively. The relative standard deviation (RSD%) for five replicate simultaneous determinations of BG and CV were 4.7% and 1.7%, respectively. Extraction efficiencies of the BG and CV dyes in the presence of interfering ions were also investigated. Sample preparation based on the quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe (QuEChERS) extraction combined with the IL-DLLME method and zero crossing first derivative spectrophotometric detection was applied for the simultaneous analysis of BG and CV in fish and water samples with quantitative recoveries.
Insights into water coordination associated with the CuII/ CuI electron transfer at a biomimetic Cu centre
Porras Gutierrez, Ana Gabriela,Zeitouny, Joceline,Gomila, Antoine,Douziech, Benedicte,Cosquer, Nathalie,Conan, Francoise,Reinaud, Olivia,Hapiot, Philippe,Le Mest, Yves,Lagrost, Corinne,Le Poul, Nicolas
, p. 6436 - 6445 (2014)
The coordination properties of the biomimetic complex [Cu(TMPA)(H 2O)](CF3SO3)2 (TMPA = tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine) have been investigated by electrochemistry combined with UV-Vis and EPR spectroscopy in different non-coordinating media including imidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquids, for different water contents. The solid-state X-ray diffraction analysis of the complex shows that the cupric centre lies in a N4O coordination environment with a nearly perfect trigonal bipyramidal geometry (TBP), the water ligand being axially coordinated to CuII. In solution, the coordination geometry of the complex remains TBP in all media. Neither the triflate ion nor the anions of the ionic liquids were found to coordinate the copper centre. Cyclic voltammetry in all media shows that the decoordination of the water molecule occurs upon monoelectronic reduction of the CuII complex. Back-coordination of the water ligand at the cuprous state can be detected by increasing the water content and/or decreasing the timescale of the experiment. Numerical simulations of the voltammograms allow the determination of kinetics and thermodynamics for the water association-dissociation mechanism. The resulting data suggest that (i) the binding/unbinding of water at the CuI redox state is relatively slow and equilibrated in all media, and (ii) the binding of water at CuI is somewhat faster in the ionic liquids than in the non-coordinating solvents, while the decoordination process is weakly sensitive to the nature of the solvents. These results suggest that ionic liquids favour water exchange without interfering with the coordination sphere of the metal centre. This makes them promising media for studying host-guest reactions with biomimetic complexes. This journal is the Partner Organisations 2014.
Correlating ionic liquid solvent effects with solvent parameters for a reaction that proceeds through a xanthylium intermediate
Gilbert, Alyssa,Bucher, G?tz,Haines, Ronald S.,Harper, Jason B.
, p. 9336 - 9342 (2019)
A unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction that proceeds through a xanthylium carbocation was studied in seven ionic liquid solvents. It was found that the general trend in the rate constant with changing proportion of ionic liquid in the reaction mixture was different to that seen for other unimolecular processes, with the rate constant increasing as more ionic liquid was added to the reaction mixture. A significant correlation was found between the natural logarithm of the rate constant and a combination of the Kamlet-Taft solvent parameters. This relationship indicated that the principal interaction involved hydrogen bonding between the ionic liquid and some species along the reaction coordinate. Further, this correlation enables prediction of the effects that other ionic liquids will have on this, and other, reactions that proceed through a similar intermediate.
Chemoselective thioacetalization and transthioacetalization of carbonyl compounds catalyzed by immobilized scandium(III) triflate in ionic liquids
Kamal, Ahmed,Chouhan, Gagan
, p. 3337 - 3340 (2003)
Immobilized scandium triflate [Sc(OTf)3] in ionic liquids has been found to be an extremely efficient and recyclable catalyst for the thioacetalization and transthioacetalization of both aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes. Significant rate acceleration and chemoselectivity was achieved by employing this catalytic system.
Interactions of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate with N,N-dimethylformamide: Density and viscosity measurements
Bennett,Dikio,Angaye,Wankasi,Dikio,Bahadur,Ebenso
, p. 661 - 666 (2016)
Physico-chemical properties: density (ρ) and viscosity (η) at (303.15, 313.15 and 323.15) K were measured for the binary mixtures of synthesized and characterized ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [BMIM][PF6] with N,N
Temperature-dependent solvatochromic probe behavior within ionic liquids and (ionic liquid + water) mixtures
Trivedi, Shruti,Malek, Naved I.,Behera, Kamalakanta,Pandey, Siddharth
, p. 8118 - 8125 (2010)
Spectroscopic responses of absorbance probes, betaine dye 33, N,N-diethyl-4-nitroaniline, and 4-nitroaniline, and fluorescence dipolarity probes, pyrene (Py) and pyrene-1-carboxaldehyde (PyCHO) within ionic liquids (ILs) 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([bmim][PF6]) and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([bmim][BF4]), and aqueous mixtures of [bmim][BF4] are used to assess the changes in important physicochemical properties with temperature in the range 10-90 ?°C. ETN obtained from betaine dye 33, indicating dipolarity/ polarizability and/or hydrogen bond donating (HBD) acidity, decreases linearly with increasing temperature within the two ILs. Changes in Kamlet-Taft parameters dipolarity/polarizability (??*), HBD acidity (?±), and HB accepting (HBA) basicity (?2) with temperature show interesting trends. While ??* and ?± decrease linearly with increasing temperature within the two ILs, ?2 appears to be independent of the temperature. Similar to ETNand ??*, the first-to-third band intensity ratio of probe Py also decreases linearly with increasing temperature within the ILs. The lowest energy fluorescence maxima of PyCHO, though it decreases significantly within water as the temperature is increased from 10 to 90 ?°C, it does not change within the two ILs investigated. The temperature dependence of the dipolarity/polarizability as manifested via betaine dye 33 behavior is found to be more within the aqueous mixtures of [bmim][BF4] as compared to that within neat [bmim][BF4] or neat water. The sensitivity of ??* toward temperature increases as IL is added to water and that of ?± decreases. The temperature dependent Py behavior shows no clear-cut trend within aqueous mixtures of [bmim][BF4]; insensitivity of the PyCHO response toward temperature change is reasserted within aqueous IL mixtures. All-in-all, the temperature-dependent behavior of solvatochromic probes within [bmim][PF6], [bmim][BF4], and aqueous mixtures of [bmim][BF4] is found to depend on the identity of the probe. ? 2010 American Chemical Society.
Solvent-solute interactions in ionic liquids
Crowhurst, Lorna,Mawdsley, Philip R.,Perez-Arlandis, Juan M.,Salter, Paul A.,Welton, Tom
, p. 2790 - 2794 (2003)
A range of ionic liquids was studied utilizing the Kamlet-Taft parameters hydrogen bond acidity (α), hydrogen bond basicity (β), and dipolarity/polarizability effects (π*). Some of the ionic liquids studied were methanol, acetonitrile, acetone, dichloromethane, toluene, hexane, and water. π* was high for all the ionic liquids investigated and varied with both anion and cation. α was generally moderate and depended chiefly on the cation. β was also moderate and depended mainly on the anion. Comparison was made with other polarity measurements in ionic liquids.
Synthesis of Zn-based metal-organic frameworks in ionic liquid microemulsions at room temperature
Ye, Ranfeng,Ni, Min,Xu, Yuanyuan,Chen, Hao,Li, Shengqing
, p. 26237 - 26242 (2018)
For the first time, Zn-metal-organic frameworks (Zn-MOFs) were prepared using Zn2+ and the aromatic ligand 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid (BTC) in ionic liquid microemulsions stabilized by the surfactant TX-100. This proposed environmentally friendly approach to synthesize Zn-MOFs is simple, requires no energy input, and operates at room temperature. The synthesized Zn-MOFs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), single crystal X-ray diffraction and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The results showed that two different Zn-MOF crystals had been successfully synthesized and that [NaZn(C9H3O6)(H2O)4]·1.5H2O was prepared by using this method for the first time. The influence of different parameters such as the pH value, the ratio of reactants, and reaction time on the morphology and size of the Zn-MOFs was studied. Long rod Zn-MOFs with an average size of ~25 μm could be obtained in the ionic liquid microemulsions with a molar ratio (organic ligand to metal ion) of 1 : 1 at pH 5.98 for 24 h. The crystal type and morphology of the Zn-MOFs could be controlled by the ionic liquid microemulsions at room temperature. This green synthesis method can be used to study their industrial production.
Dynamic solvation in room-temperature ionic liquids
Chowdhury,Halder,Sanders,Calhoun,Anderson,Armstrong,Song,Petrich
, p. 10245 - 10255 (2004)
The dynamic solvation of the fluorescent probe, coumarin 153, is measured in five room-temperature ionic liquids using different experimental techniques and methods of data analysis. With time-resolved stimulated-emission and time-correlated single-photon counting techniques, it is found that the solvation is comprised of an initial rapid component of a??55 ps. In all the solvents, half or more of the solvation is completed within 100 ps. The remainder of the solvation occurs on a much longer time scale. The emission spectra of coumarin 153 are nearly superimposable at all temperatures in a given solvent unless they are obtained using the supercooled liquid, suggesting that the solvents have an essentially glassy nature. The physical origin of the two components is discussed in terms of the polarizability of the organic cation for the faster one and the relative diffusional motion of the cations and the anions for the slower one. A comparison of the solvation response functions obtained from single-wavelength and from spectral-reconstruction measurements is provided. Preliminary fluorescence-upconversion measurements are presented against which the appropriateness of the single-wavelength method for constructing solvation correlation functions and the use of stimulated-emission measurements is considered. These measurements are consistent with the trends mentioned above, but a comparison indicates that the presence of one or more excited states distorts the stimulated-emission kinetics such that they do not perfectly reproduce the spontaneous emission data. Fluorescence-upconversion results indicate an initial solvation component on the order of a??7 ps.
Label-free polypeptide-based enzyme detection using a graphene-nanoparticle hybrid sensor
Myung, Sung,Yin, Perry T.,Kim, Cheoljin,Park, Jaesung,Solanki, Aniruddh,Reyes, Pavel Ivanoff,Lu, Yicheng,Kim, Kwang S.,Lee, Ki-Bum
, p. 6081 - 6087 (2012)
A graphene-nanoparticle (NP) hybrid biosensor that utilizes an electrical hysteresis change to detect the enzymatic activity and concentration of Carboxypeptidase B was developed. The results indicate that the novel graphene-NP hybrid biosensor, utilizing
Synthesis and physical-chemical properties of ionic liquids based on 1- n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium cation
Suarez,Einloft,Dullius,De Souza,Dupont
, p. 1626 - 1639 (1998)
The reaction of 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BMI.Cl) with sodium tetrafluoroborate or sodium hexafluorophosphate affords the molten salts BMI.X (1, X = BF4 and 2, X = PF6). Compounds 1 and 2 are viscous liquids within a wide range of temperature (down to 192 K). IR, NMR, density, viscosity and conductivity measurements suggest that compound 2 behaves quasi-molecular. Compound 1 is quasi-molecular below 279 K, but at higher temperatures is probably composed of imidazolium and tetrafluoroborate ions in an extended hydrogen-bonded network.
Influence of structural variation in room-temperature ionic liquids on the selectivity and efficiency of competitive alkali metal salt extraction by a crown ether
Chun,Dzyuba,Bartsch
, p. 3737 - 3741 (2001)
An improved method for the preparation of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphates provides a series of room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) in which the 1-alkyl group is varied systematically from butyl to nonyl. For competitive solvent extraction of aqueous solutions of alkali metal chlorides with solutions of dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DC18C6) in these RTILs, the extraction efficiency generally diminished as the length of the 1-alkyl group was increased. Under the same conditions, extraction of alkali metal chlorides into solutions of DC18C6 in chloroform, nitrobenzene, and 1-octanol was undetectable. The extraction selectivity order for DC18C6 in the RTILs was K+ > Rb+ > Cs+ > Na+ > Li+. As the alkyl group in the RTIL was elongated, the K+/Rb+ and K+/Cs+ selectivities exhibited general increases with the larger enhancement for the latter. For DC18C6 in 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, the alkali metal cation extraction selectivity and efficiency were unaffected by variation of the aqueous-phase anion from chloride to nitrate to sulfate.
Biosynthesis of glycyrrhetic acid 3-O-mono-β-d-glucuronide catalyzed by β-d-glucuronidase with enhanced bond selectivity in an ionic liquid/buffer biphasic system
He, Dong-Mei,Kaleem, Imdad,Qin, Si-Ying,Dai, Da-Zhang,Liu, Gui-Yan,Li, Chun
, p. 1916 - 1922 (2010)
The bond selective hydrolysis of glycyrrhizin (GL) to glycyrrhetic acid 3-O-mono-β-d-glucuronide (GAMG) catalyzed by recombinant β-d-glucuronidase from Escherichia coli BL21 (PGUS-E) was successfully performed in an ionic liquid (IL)/buffer biphasic system. Five ILs were analyzed, however, a hydrophobic IL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([BMIM]PF6) showed the best biocompatibility with PGUS-E. An obvious enhancement in the initial reaction rate, substrate conversion, GAMG yield and chemical bond selectivity (Scb) was observed using 40% (v/v) [BMIM]PF6/buffer as the reaction medium when compared to the acetate buffer medium. Under the optimized conditions (pH 6.0, temperature 50°C, substrate concentration 6mM and shaking speed 200rpm), the initial reaction rate, the GAMG yield and the Scb reached 3.15mMh-1, 74.36% and 98.12%, respectively. The recyclability of [BMIM]PF6 was also studied and found to be reusable for five batches with high recovery percentage (≥92%). Furthermore, the desired product and byproduct were easily separated since they were distributed in different phases. Additionally, higher Vmax (3.14 versus 2.24mMh-1), lower apparent Km (1.21 versus 1.80mM) and Ea (25.97 versus 32.60kJmol-1) were achieved in [BMIM]PF6/buffer biphasic system than that in monophasic buffer system.
Thermodynamic investigation of room temperature ionic liquid : the heat capacity and thermodynamic functions of BMIPF6
Zhang, Z. H.,Zhang, J. L.,Xiong, H.,Li, G. P.,Cui, T.,Sun, L. X.,Xu, F.,Cao, Z.,Li, F.,Zhao, J. J.
, p. 1143 - 1148 (2010)
The molar heat capacities of the room temperature ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluoroborate (BMIPF6) were measured by an adiabatic calorimeter in temperature range from 80 to 390 K. The dependence of the molar heat capacity on temperature is given as a function of the reduced temperature (X) by polynomial equations, C P,m (J K -1 mol-1) = 204.75 + 81.421X - 23.828 X 2 + 12.044X 3 + 2.5442X 4 [X = (T - 132.5)/52.5] for the solid phase (80-185 K), C P,m (J K-1 mol-1) = 368.99 + 2.4199X + 1.0027X 2 + 0.43395X 3 [X = (T - 230)/35] for the glass state (195 - 265 K), and C P,m (J K-1 mol -1) = 415.01 + 21.992X - 0.24656X 2 + 0.57770X 3 [X = (T - 337.5)/52.5] for the liquid phase (285-390 K), respectively. According to the polynomial equations and thermodynamic relationship, the values of thermodynamic function of the BMIPF6 relative to 298.15 K were calculated in temperature range from 80 to 390 K with an interval of 5 K. The glass transition of BMIPF6 was measured to be 190.41 K, the enthalpy and entropy of the glass transition were determined to be ΔH g = 2.853 kJ mol-1 and ΔS g = 14.98 J K-1 mol-1, respectively. The results showed that the milting point of the BMIPF6 is 281.83 K, the enthalpy and entropy of phase transition were calculated to be ΔH m = 20.67 kJ mol-1 and ΔS m = 73.34 J K-1 mol -1.
Convenient synthesis of various ionic liquids from onium hydroxides and ammonium salts
Peng, Yanqing,Li, Guiyun,Li, Jianguo,Yu, Shaojun
, p. 4286 - 4288 (2009)
Hydroxide ionic liquids, such as 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium hydroxides, undergo smooth anion metathesis with ammonium salts to produce a variety of ionic liquids in excellent yields. It is a practical supplement of traditional neutralization method due to the broader range of starting materials containing desired anions.
Utilisation of 1,3-dialkylimidazolium-2-carboxylates as CO 2-carriers in the presence of Na+ and K+: Application in the synthesis of carboxylates, monomethylcarbonate anions and halogen-free ionic liquids
Tommasi, Immacolata,Sorrentino, Fabiana
, p. 2141 - 2145 (2005)
1,3-Dialkylimidazolium-2-carboxylate compounds have recently been fully characterised. Here we describe the utilisation of 1,3-dimethyl (1a) and 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium-2-carboxylate (1b) in a carboxylation reaction with transfer of the CO2 moiety to benzoylacetone and methanol for the synthesis, in high yield, of benzoylacetate and monoalkylcarbonate anions, respectively. Conversely, when compounds 1a and b are reacted with carbonylic substrates lacking C-H active bonds, a product resulting from nucleophilic attack of the 1,3-dialkylimidazol-2-ylidene species on the carbonyl moiety is obtained. The reported reactions can find applications in organic synthesis and in the synthesis of halogen-free ionic liquids.
Probing the importance of ionic liquid structure: A general ionic liquid effect on an SNAr process
Tanner, Eden E. L.,Hawker, Rebecca R.,Yau, Hon Man,Croft, Anna K.,Harper, Jason B.
, p. 7516 - 7521 (2013)
The effect of a range of ionic liquids, with systematic variations in the cation and anion, on the rate constant of an aromatic substitution process was investigated. Temperature-dependent kinetic data allowed calculation of activation parameters for the process in each solvent. These data demonstrate a generalised ionic liquid effect, with an increase in rate constant observed in each ionic solvent, though the microscopic origins of the rate constant enhancement differ with the nature of the ionic liquid.
Surface spectroscopy of room-temperature ionic liquids on a platinum electrode: A sum frequency generation study
Rivera-Rubero, Selimar,Baldelli, Steven
, p. 15133 - 15140 (2004)
Sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy (SFG) and cyclic voltammetry (CV) measurements have been conducted on the ionic liquid/platinum electrode system. The room-temperature ionic liquid investigated is 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium [BMIM]+ with [PF6]- or [BF4]- anions. SFG spectra are taken in situ under potential control from 2750 to 3300 cm-1 (C-H stretching region). Polarization-dependent SFG spectra are used to extract orientation information for the cation at the electrode surface. The SFG spectra indicate that the cation changes orientation as the electrode potential is changed within the double-layer region. The plane of the imidazolium ring tips from 35?° at positive surface charge to a??60?° from the surface normal at negative surface charge. Further, the orientation change is different for [BMIM][PF 6] than for [BMIM][BF4]. A model for ions at the surface is presented based on these spectroscopic and electrochemical measurements.
β-Diimine-methallyl nickel complexes in ionic liquid: A biphasic green system for the high selective styrene dimerization
Landolsi, Kamel,Msaddek, Moncef
, (2022/02/23)
The selective head-to-tail dimerization of styrene to 1,3-diphenyl-1-butene over [Ni(β-diimine)- (methallyl)]+PF6- / Et2O?HBF4 catalyst system has been investigated. The styrene conversion up to 95 % and the TOF (TOF = 508 h?1) were reached after optimization of the reaction parameters (temperature: T = 80 °C; time: t = 1 h…) with selectivity to E-1,3-diphényl-1-butene stereoisomer up to 98%. Solvents and diimine ligands have a strong effect on the catalyst activity. The substituents on the β-diimine ligands have a crucial effect on the conversion but did not affect the selectivity. Cationic β-diimine-nickel (2 + ) is the likely active species. Reaction products were characterized by 1H and 13C NMR, IR, and GC–MS spectroscopies.
Convenient synthesis of long alkyl-chain triazolylglycosides using ionic liquid as dual promoter-solvent: Readily access to non-ionic triazolylglycoside surfactants for evaluation of cytotoxic activity
Ketsomboon, Nutthanicha,Saeeng, Rungnapha,Sirion, Uthaiwan,Srisook, Klaokwan
, (2021/08/26)
A convenient method for the one-pot synthesis of long alkyl-chain triazolylglycosides using ionic liquid as dual promoter and solvent is described via a sequential one-pot two-step glycosidation-CuAAc click reaction. The reaction was carried out using commercially available substrates, including glycosyl bromides, sodium azide and various long alkyl-chain alkynes to achieve the corresponding products in moderate to high yields. Furthermore, this approach was successfully applied for the preparation of non-ionic monocatenary triazolylglycoside surfactants in excellent yields through simple deacetylation. Subsequently, these surfactants were further evaluated for their cytotoxic activity.
Red Propolis as a Source of Antimicrobial Phytochemicals: Extraction Using High-Performance Alternative Solvents
dos Santos, Cíntia M.,de Souza Mesquita, Leonardo M.,Braga, Anna Rafaela C.,de Rosso, Veridiana V.
, (2021/06/28)
Propolis is a resinous material rich in flavonoids and involved in several biological activities such as antimicrobial, fungicide, and antiparasitic functions. Conventionally, ethanolic solutions are used to obtain propolis phytochemicals, which restrict their use in some cultures. Given this, we developed an alcohol-free high-performance extractive approach to recover antibacterial and antioxidants phytochemicals from red propolis. Thus, aqueous-solutions of ionic liquids (IL) and eutectic solvents were used and then tested for their total flavonoids, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities. The surface-responsive technique was applied regarding some variables, namely, the time of extraction, the number of extractions, and cavitation power (W), to optimize the process (in terms of higher yields of flavonoids and better antioxidant activity). After that, four extractions with the same biomass (repetitions) using 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [C6mim]Cl, under the operational conditions fixed at 3.3 min and 300 W, were able to recover 394.39 ± 36.30 mg RuE. g?1 of total flavonoids, with total antioxidant capacity evaluated up to 7595.77 ± 5.48 μmol TE. g?1dried biomass, besides inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enteritidis bacteria (inhibition halo of 23.0 ± 1.0 and 15.7 ± 2.1, respectively). Aiming at the development of new technologies, the antimicrobial effect also presented by [C6mim]Cl may be appealing, and future studies are required to understand possible synergistic actions with propolis phytochemicals. Thereby, we successfully applied a completely alcohol-free method to obtain antimicrobials phytochemicals and highly antioxidants from red propolis, representing an optimized process to replace the conventional extracts produced until now.
174501-64-5 Process route
-

- 616-47-7
1-methyl-1H-imidazole

-

- 109-65-9
1-bromo-butane

-

- 174501-64-5
3-butyl-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; at 40 - 120 ℃; for 0.166667h; microwave irradiation; sonication;
|
94% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; at 80 ℃; for 3.5h;
|
93% |
|
With ammonium hexafluorophosphate; 3-butyl-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate; at 80 ℃; for 15h;
|
89% |
|
1-methyl-1H-imidazole; With potassium hexafluorophosphate; at 80 ℃; for 12h;
1-bromo-butane; In water;
|
86% |
|
1-methyl-1H-imidazole; 1-bromo-butane; at 140 ℃;
With hexafluorophosphoric acid; In water; for 0.166667h; Further stages.;
|
64% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 84 ℃; for 3h; sonification;
|
61% |
|
1-methyl-1H-imidazole; 1-bromo-butane; In toluene; at 90 ℃; for 2h;
With hexafluorophosphoric acid; In water; Further stages.;
|
-

- 85100-77-2
1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolim bromide

-

- 174501-64-5
3-butyl-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃;
|
100% |
|
With ammonium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
91% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 24h;
|
87% |
|
With hexafluorophosphoric acid; In water;
|
79% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In dichloromethane; for 48h;
|
78% |
|
With ammonium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
75% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 18h;
|
73% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 24h;
|
70% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 16h;
|
61% |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
59% |
|
With hexafluorophosphoric acid; In water; at 20 ℃; for 4h;
|
52% |
|
With ammonium hexafluorophosphate;
|
|
|
With hexafluorophosphoric acid; In water; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
1.58 mmol |
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate;
|
|
|
With sodium hexaflorophosphate; at 100 ℃; for 0.25h; Microwave irradiation; Neat (no solvent);
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; at 20 ℃; for 6h;
|
|
|
With sodium hexaflorophosphate; In water;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; at 20 ℃; for 5h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 80 ℃; for 3h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In methanol; at 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In acetone; at 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In acetone; at 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In water; at 20 ℃; for 24h;
|
|
|
With hexafluorophosphoric acid; In acetone; at 20 ℃; for 24h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In acetone; at 20 ℃; for 2h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; In acetone; at 40 ℃; for 10h;
|
|
|
With potassium hexafluorophosphate; Inert atmosphere;
|
174501-64-5 Upstream products
-
79917-90-1

1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride
-
616-47-7

1-methyl-1H-imidazole
-
109-65-9

1-bromo-butane
-
109-69-3

n-Butyl chloride
174501-64-5 Downstream products
-
616-47-7

1-methyl-1H-imidazole
-
106-98-9

1-butylene
-
2366-52-1

1-fluorobutane
-
79973-42-5

bis(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)cobalt(III) hexafluorophosphate
Relevant Products
-
433337-11-2CAS NO.: 433337-11-2
CAS:433337-11-2
-
1-Dodecanaminium,N,N,N-trimethyl-, bromide (1:1)
CAS:1119-94-4