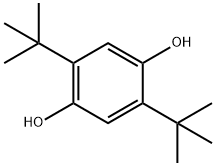
88-58-4
- Product Name:1,4-Benzenediol,2,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-
- Molecular Formula:C14H22O2
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 88-58-4
Molecular Formula: C14H22O2
Appearance: White or light yellow crystals
88-58-4 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C14H22O2
- Molecular Weight:222.327
- Appearance/Colour:White or light yellow crystals
- Vapor Pressure:6.6E-05mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:216-218 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.52
- Boiling Point:334.4 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:11.89±0.23(Predicted)
- Flash Point:151.5 °C
- PSA:40.46000
- Density:1.012 g/cm3
- LogP:3.69280
88-58-4 Usage
Chemical Properties
cream or pale brown solid
Uses
2,5-Di-tert-butylhydroquinone is the oxidation substrate used to measure the catalytic activity of the copper(II) enzyme-like catalysts.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of hydroquinones that is benzene-1,4-diol substituted by tert-butyl groups at position 2 and 5.
General Description
Mobilizes Ca2+ specifically from the Ins(1,4,5)P3-sensitive Ca2+ stores by inhibiting microsomal and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase activity. Does not affect mitochondrial Ca2+ fluxes or plasma membrane Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase activity. Useful for the study of endomembrane Ca2+ stores and plasma membrane Ca2+ permeability pathways.
Biological Activity
A selective inhibitor of endoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ -ATPase.
Biochem/physiol Actions
2,5-Di-tert-butylhydroquinone specifically inhibits the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ uptake in the rat ventricle.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the hydroquinone from *C6H6 or AcOH. [Beilstein 6 III 4741.]
references
[1]. hasséssian h, vaca l, kunze dl. blockade of the inward rectifier potassium current by the ca(2+)-atpase inhibitor 2',5'-di(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone (bhq). br j pharmacol, 1994, 112(4): 1118-1122.[2]. fusi f, gorelli b, valoti m, et al. effects of 2,5-di-t-butyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone (bhq) on rat aorta smooth muscle. eur j pharmacol, 1998, 346(2-3): 237-243.[3]. fusi f, saponara s, gagov h, et al. 2,5-di-t-butyl-1,4-benzohydroquinone (bhq) inhibits vascular l-type ca(2+) channel via superoxide anion generation. br j pharmacol, 2001, 133(7): 988-996.[4]. jan cr, ho cm, wu sn, et al. mechanism of rise and decay of 2,5-di-tert-butylhydroquinone-induced ca2+ signals in madin darby canine kidney cells. eur j pharmacol, 1999, 365(1): 111-117.
InChI:InChI=1/C14H22O2/c1-13(2,3)9-7-12(16)10(8-11(9)15)14(4,5)6/h7-8,15-16H,1-6H3
88-58-4 Relevant articles
Preparation method of 2, 5-di-tert-butyl-p-dimethoxybenzene
-
Paragraph 0033-0035; 0038-0040; 0043-0045; 0048-0050; 0053, (2021/06/02)
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2, 5-di-tert-butyl-p-dimethoxybenzene, which comprises the following steps: (1) reacting tert-butyl alcohol with hydroquinone in a first solvent under the action of a first catalyst, cooling and crystallizing after the reaction is finished, filtering, washing and drying to obtain 2,5-di-tert-butyl hydroquinone; and (2) reacting the 2, 5-di-tert-butyl hydroquinone obtained in the step (1) with methyl iodide in a second solvent under the action of a second catalyst, cooling to room temperature after the reaction is finished, adding brine and an organic solvent into the reaction liquid for extraction, washing the obtained organic layer, and performing vacuum drying to obtain the 2, 5-di-tert-butyl-p-dimethoxybenzene product. The method has the advantages of simple process, mild reaction conditions, environmental protection, low cost and high yield.
A PROCESS FOR PREPARATION OF TERTIARY BUTYL HYDROQUINONE
-
Page/Page column 9; 10; 11, (2020/07/15)
A PROCESS FOR PREPARATION OF TERTIARY BUTYL HYDROQUINONE The present invention relates to a process for preparation of tertiary butyl hydroquinone. More particularly, it relates to a process for preparation 5 of TBHQ by eradicating the consumption of hazardous solvents like toluene and eliminating hazardous impurities like hydroquinone, tertiary butyl‐p‐benzoquinone and also drastically reducing the presence of heavy metals like lead and arsenic. The present invention includes stages I‐IV in which TBHQ is more purified and precipitated with a high scale purity results. TBHQ has 10 application in food additives, animal feeds, as an antioxidant, emulsifier and in edible oils, effectively as antioxidant.
1-Methyl-1,4-cyclohexadiene as a Traceless Reducing Agent for the Synthesis of Catechols and Hydroquinones
Baschieri, Andrea,Amorati, Riccardo,Valgimigli, Luca,Sambri, Letizia
, p. 13655 - 13664 (2019/10/28)
Pro-aromatic and volatile 1-methyl-1,4-cyclohexadiene (MeCHD) was used for the first time as a valid H-atom source in an innovative method to reduce ortho or para quinones to obtain the corresponding catechols and hydroquinones in good to excellent yields. Notably, the excess of MeCHD and the toluene formed as the oxidation product can be easily removed by evaporation. In some cases, trifluoroacetic acid as a catalyst was added to obtain the desired products. The reaction proceeds in air and under mild conditions, without metal catalysts and sulfur derivatives, resulting in an excellent and competitive method to reduce quinones. The mechanism is attributed to a radical reaction triggered by a hydrogen atom transfer from MeCHD to quinones, or, in the presence of trifluoroacetic acid, to a hydride transfer process.
Reactivity of iPrPCPIrH4 with para-benzoquinones
Wilklow-Marnell, Miles,Brennessel, William W.,Jones, William D.
, p. 209 - 214 (2017/11/24)
In the interest of investigating new hydrogen acceptors for pincer–iridium catalyzed dehydrogenations with the ability to be catalytically recycled, a series of para-benzoquinones have been reacted with iPrPCPIrH4 in various solvents and conditions. Preliminary results indicate that a wide range of quinones are capable of dehydrogenating iPrPCPIrH4, and that several turn-overs in alcohol dehydrogenation by iPrPCPIr are possible at room temperature using benzoquinone acceptors. However, strong acceptor–catalyst interactions are inhibitory toward catalysis when the acceptor is used in excess. A new class of (bis)-η2 pi-adducts, formed between iPrPCPIr and benzoquinones, nicknamed “barber-chairs”, has been identified and 3 examples have been characterized.
88-58-4 Process route
-

-
acid blue 5

-

- 1450-72-2
5-methyl-2-hydroxyacetophenone

-

- 591-81-1
4-hydroxybutanoic acid

-

- 617-48-1,78644-42-5
malic acid

-

- 19071-34-2
2-hydroxyacrylic acid

-

- 83-56-7
1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene

-

- 88-58-4
2,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1,4-benzenediol

-

-
1-aminoethenol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With dihydrogen peroxide; pH=3; Reagent/catalyst; Concentration; pH-value; Kinetics;
|
-

- 1634-04-4
tert-butyl methyl ether

-

- 123-31-9,8027-02-9
hydroquinone

-

- 2444-28-2
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenol

-

- 88-58-4
2,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1,4-benzenediol

-

- 2460-87-9
4-(tert-butoxy)phenol

-

- 1948-33-0
tert-butylhydroquinone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With 3-(4-sulfobutylamino)propylsilanized MCM-41; In nitrobenzene; at 150 ℃; for 0.133333h; Concentration; chemoselective reaction; Catalytic behavior; Microwave irradiation; Green chemistry;
|
88-58-4 Upstream products
-
2460-77-7

2,5-di-tert-butyl-p-benzoquinone
-
507-20-0

tertiary butyl chloride
-
123-31-9

hydroquinone
-
115-11-7

isobutene
88-58-4 Downstream products
-
2460-77-7

2,5-di-tert-butyl-p-benzoquinone
-
124700-28-3

2,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy-phenoxyl
-
900-02-7

1,4-diacetoxy-2,5-di-tert-butyl-benzene
-
7323-63-9

1,4-di-tert-butyl-2,5-dimethoxybenzene
Relevant Products
-
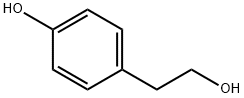
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
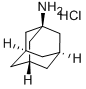
1-Adamantanamine hydrochloride
CAS:665-66-7
-
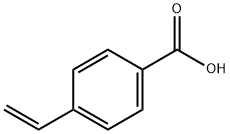
4-Vinylbenzoic acid
CAS:1075-49-6