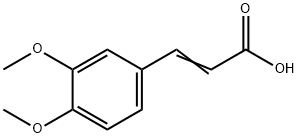
2316-26-9
- Product Name:3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid
- Molecular Formula:C11H12O4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 2316-26-9
Molecular Formula: C11H12O4
Appearance: Slightly yellow to light beige powder
2316-26-9 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C11H12O4
- Molecular Weight:208.214
- Appearance/Colour:Slightly yellow to light beige powder
- Vapor Pressure:4.8E-06mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:181-183 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.4389 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:367.4oCat 760 mmHg
- PKA:4.53±0.10(Predicted)
- Flash Point:144oC
- PSA:55.76000
- Density:1.203 g/cm3
- LogP:1.80160
2316-26-9 Usage
Chemical Properties
Slightly yellow to light beige powder
Uses
3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic Acid is a Cinnamic Acid (C442030) derivative,used in the synthesis of amides and esters through coupling reactions involving carboxylic acids and amines and N-methylation of amides and O-methylation of carboxylic acids.
InChI:InChI=1/C11H12O4/c1-14-9-5-3-8(4-6-11(12)13)7-10(9)15-2/h3-7H,1-2H3,(H,12,13)/p-1/b6-4+
2316-26-9 Relevant articles
Separation and identification of an impurity from the istradefylline intermediate
Meng, Zihui,Wang, Hongyi,Wang, Yiyun,Xu, Haojie,Xu, Zhibin,Xue, Min,Zheng, Zhonghui
, p. 14493 - 14499 (2020)
Istradefylline is a selective adenosine antagonist for the A2a receptor, and it is used to treat the Parkinson's disease and improve dyskinesia in the early stage of the Parkinson's disease. An impurity in the istradefylline intermediate A1 (6-amino-1,3-diethyl-2,4-(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione) was identified by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); it was separated by preparative HPLC and further characterized by UV, IR, MS, NMR, 2D NMR and single-crystal XRD analyses. The impurity was identified as (E)-N-ethyl-2-cyano-3-ethylamino-2-butenamide, which originated from the synthetic process of the intermediate A1. The structure of this impurity might affect the efficiency and safety of istradefylline; therefore, the research and control of this impurity are necessary for ensuring the quality of istradefylline.
Design and synthesis of caffeic acid derivatives and evaluation of their inhibitory activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Chen, Hong-geng,Chen, Wei-min,Liu, Wei-liang,Su, Ya-lun,Sun, Ping-hua,Zeng, Shao-gao,Zeng, Yun-feng,Zheng, Jun-xia,Zhou, Hai-bo
, p. 177 - 194 (2022/01/08)
Bacteria need to transmit autoinducers to each other through a quorum sensing system. When the concentration of signal molecule reaches a threshold, it affects the expression of specific genes in bacteria, thereby improving the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics, promoting the formation of biofilms, and producing virulence factors. In this paper, various caffeic acid derivatives were synthesized based on functional groups. The results of growth curve and minimal inhibitory concentration proved that the derivatives did not affect the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Therefore, the inhibitory effects of the derivatives on biofilms and virulence factors were further evaluated. Among these derivatives examined, compound F-17 (4-bromophenethyl-3-(3, 4-dihydroxy-phenyl)acrylate) showed very significant inhibitory effect on biofilm, elastase, pyocyanin, and swarming motility. Molecular docking and calculation of binding free energy of F-17 also showed a good binding effect on LasR and PqsR. In addition, compound F-17 has no obvious cytotoxicity. These experimental results show that F-17 is a potential virulence factor inhibitor. [Figure not available: see fulltext.]
One-Pot Biocatalytic In Vivo Methylation-Hydroamination of Bioderived Lignin Monomers to Generate a Key Precursor to L-DOPA
Birmingham, William R.,Galman, James L.,Parmeggiani, Fabio,Seibt, Lisa,Turner, Nicholas J.
, (2022/01/13)
Electron-rich phenolic substrates can be derived from the depolymerisation of lignin feedstocks. Direct biotransformations of the hydroxycinnamic acid monomers obtained can be exploited to produce high-value chemicals, such as α-amino acids, however the reaction is often hampered by the chemical autooxidation in alkaline or harsh reaction media. Regioselective O-methyltransferases (OMTs) are ubiquitous enzymes in natural secondary metabolic pathways utilising an expensive co-substrate S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM) as the methylating reagent altering the physicochemical properties of the hydroxycinnamic acids. In this study, we engineered an OMT to accept a variety of electron-rich phenolic substrates, modified a commercial E. coli strain BL21 (DE3) to regenerate SAM in vivo, and combined it with an engineered ammonia lyase to partake in a one-pot, two whole cell enzyme cascade to produce the l-DOPA precursor l-veratrylglycine from lignin-derived ferulic acid.
In quest of small-molecules as potent non-competitive inhibitors against influenza
Malbari, Khushboo,Saha, Priyanka,Chawla-Sarkar, Mamta,Dutta, Shanta,Rai, Swita,Joshi, Mamata,Kanyalkar, Meena
, (2021/07/19)
A series of scaffolds namely aurones, 3-indolinones, 4-quinolones and cinnamic acid-piperazine hybrids, was designed, synthesized and investigated in vitro against influenza A/H1N1pdm09 virus. Designed molecules adopted different binding mode i.e., in 430-cavity of neuraminidase, unlike sialic acid and oseltamivir in molecular docking studies. All molecules reduced the viral titer and exhibited non-cytotoxicity along with cryo-protective property towards MDCK cells. Molecules (Z)-2-(3′-Chloro-benzylidene)-1,2-dihydro-indol-3-one (2f), (Z)-2-(4′-Chloro-benzylidene)-1,2-dihydro-indol-3-one (2g) and 2-(2′-Methoxy-phenyl)-1H-quinolin-4-one (3a) were the most interesting molecules identified in this research, endowed with robust potencies showing low-nanomolar EC50 values of 4.0 nM, 6.7 nM and 4.9 nM, respectively, compared to reference competitive and non-competitive inhibitors: oseltamivir (EC50 = 12.7 nM) and quercetin (EC50 = 0.56 μM), respectively. Besides, 2f, 2g and 3a exhibited good neuraminidase inhibitory activity in sub-micromolar range (IC50 = 0.52 μM, 3.5 μM, 1.3 μM respectively). Moreover, these molecules were determined as non-competitive inhibitors similar to reference non-competitive inhibitor quercetin unlike reference competitive inhibitor oseltamivir in kinetics studies.
Photo-Promoted Decarboxylative Alkylation of α, β-Unsaturated Carboxylic Acids with ICH2CN for the Synthesis of β, γ-Unsaturated Nitriles
Pan, Chunxiang,Yang, Chunhui,Li, Kangkui,Zhang, Keyang,Zhu, Yuanbin,Wu, Shiyuan,Zhou, Yongyun,Fan, Baomin
supporting information, p. 7188 - 7193 (2021/10/01)
An efficient, catalyst/photocatalyst-free, and cost-effective methodology for the decarboxylative alkylation of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids to synthesize β,γ-unsaturated nitriles has been developed. The reaction proceeded in an environmentally benign atmosphere of blue light-emitting diode irradiation with K2CO3 and water at room temperature. The methodology worked for a wide range of substrates (22 examples) with up to 83% yield. The protocol is also compatible for gram-scale synthesis.
2316-26-9 Process route
-

- 120-14-9
3,4-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde

-

- 2316-26-9
3,4-dimethoxycinnamic acid

-

- 93-07-2
Veratric acid

-

- 93-03-8
(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methanol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
-

- 331-39-5,501-16-6
caffeic acid

-

- 74-88-4
methyl iodide

-

- 2316-26-9
3,4-dimethoxycinnamic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
caffeic acid; methyl iodide; With potassium carbonate; In acetone; Reflux;
In methanol; at 20 ℃; for 10h; Alkaline conditions;
With hydrogenchloride; In methanol; water; at 20 ℃;
|
70% |
2316-26-9 Upstream products
-
110-89-4

piperidine
-
110-86-1

pyridine
-
141-82-2

malonic acid
-
120-14-9

3,4-dimethoxy-benzaldehyde
2316-26-9 Downstream products
-
2107-70-2

3,4-methoxycinnamic acid
-
97243-37-3

3-(3',4'-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dibromopropanoic acid
-
88909-07-3

(E)-3-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acrylic anhydride
Relevant Products
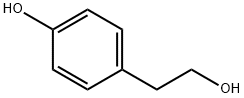
-
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
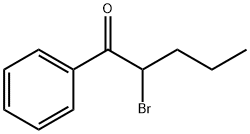
1-Pentanone, 2-bromo-1-phenyl-
CAS:49851-31-2
-
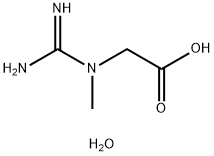
Creatine monohydrate
CAS:6020-87-7