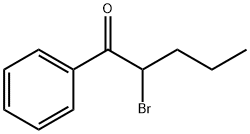
49851-31-2
- Product Name:1-Pentanone, 2-bromo-1-phenyl-
- Molecular Formula:C11H13BrO
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 49851-31-2
Molecular Formula: C11H13BrO
49851-31-2 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C11H13BrO
- Molecular Weight:241.128
- Vapor Pressure:0.003mmHg at 25°C
- Boiling Point:282.267oC at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:42.513oC
- PSA:17.07000
- Density:1.31g/cm3
- LogP:3.43290
49851-31-2 Usage
Chemical Properties
Yellow Oil
Uses
Valerophenone (V091450) derivative.
InChI:InChI=1/C11H13BrO/c1-2-6-10(12)11(13)9-7-4-3-5-8-9/h3-5,7-8,10H,2,6H2,1H3
49851-31-2 Relevant articles
Enantioconvergent Cu-Catalyzed Radical C-N Coupling of Racemic Secondary Alkyl Halides to Access α-Chiral Primary Amines
Cheng, Jiang-Tao,Dong, Xiao-Yang,Gu, Qiang-Shuai,Li, Zhong-Liang,Liu, Juan,Liu, Xin-Yuan,Luan, Cheng,Wang, Fu-Li,Wang, Li-Lei,Yang, Ning-Yuan,Zhang, Yu-Feng
supporting information, p. 15413 - 15419 (2021/09/30)
α-Chiral alkyl primary amines are virtually universal synthetic precursors for all other α-chiral N-containing compounds ubiquitous in biological, pharmaceutical, and material sciences. The enantioselective amination of common alkyl halides with ammonia is appealing for potential rapid access to α-chiral primary amines, but has hitherto remained rare due to the multifaceted difficulties in using ammonia and the underdeveloped C(sp3)-N coupling. Here we demonstrate sulfoximines as excellent ammonia surrogates for enantioconvergent radical C-N coupling with diverse racemic secondary alkyl halides (>60 examples) by copper catalysis under mild thermal conditions. The reaction efficiently provides highly enantioenrichedN-alkyl sulfoximines (up to 99% yield and >99% ee) featuring secondary benzyl, propargyl, α-carbonyl alkyl, and α-cyano alkyl stereocenters. In addition, we have converted the masked α-chiral primary amines thus obtained to various synthetic building blocks, ligands, and drugs possessing α-chiral N-functionalities, such as carbamate, carboxylamide, secondary and tertiary amine, and oxazoline, with commonly seen α-substitution patterns. These results shine light on the potential of enantioconvergent radical cross-coupling as a general chiral carbon-heteroatom formation strategy.
NBS-mediated synthesis of β-keto sulfones from benzyl alcohols and sodium arenesulfinates
Muneeswara, Madithedu,Sundaravelu, Nallappan,Sekar, Govindasamy
supporting information, p. 3479 - 3484 (2019/05/21)
An efficient synthetic route towards the synthesis of β-keto sulfones has been developed from secondary benzyl alcohols using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS). The present protocol utilizes NBS as oxidant as well as brominating agent, readily accessible benzyl alcohols and sodium arenesulfinates as the sulfonylating reagent under mild conditions. The control experiments revealed that the reaction proceeds via oxidation of alcohol to ketone, α-bromination of ketone and nucleophilic substitution by sodium arenesulfinate. Furthermore, the efficiency of the methodology was tested with a gram scale reaction and also shown the synthetic utility.
Novel benzene-based carbamates for ache/bche inhibition: Synthesis and ligand/structure-oriented sar study
Bak, Andrzej,Kozik, Violetta,Kozakiewicz, Dariusz,Gajcy, Kamila,Strub, Daniel Jan,Swietlicka, Aleksandra,Stepankova, Sarka,Imramovsky, Ales,Polanski, Jaroslaw,Smolinski, Adam,Jampilek, Josef
, (2019/05/10)
A series of new benzene-based derivatives was designed, synthesized and comprehensively characterized. All of the tested compounds were evaluated for their in vitro ability to potentially inhibit the acetyl-and butyrylcholinesterase enzymes. The selectivity index of individual molecules to cholinesterases was also determined. Generally, the inhibitory potency was stronger against butyryl-compared to acetylcholinesterase; however, some of the compounds showed a promising inhibition of both enzymes. In fact, two compounds (23, benzyl ethyl(1-oxo-1-phenylpropan-2-yl)carbamate and 28, benzyl (1-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl) (methyl)carbamate) had a very high selectivity index, while the second one (28) reached the lowest inhibitory concentration IC50 value, which corresponds quite well with galanthamine. Moreover, comparative receptor-independent and receptor-dependent structure–activity studies were conducted to explain the observed variations in inhibiting the potential of the investigated carbamate series. The principal objective of the ligand-based study was to comparatively analyze the molecular surface to gain insight into the electronic and/or steric factors that govern the ability to inhibit enzyme activities. The spatial distribution of potentially important steric and electrostatic factors was determined using the probability-guided pharmacophore mapping procedure, which is based on the iterative variable elimination method. Additionally, planar and spatial maps of the host–target interactions were created for all of the active compounds and compared with the drug molecules using the docking methodology.
Synthesis of α,β-dibromo ketones by photolysis of α-bromo ketones with N-bromosuccinimide: Photoinduced β-bromination of α-bromo ketones
Moon, Da Yoon,An, Sejin,Park, Bong Ser
, (2019/10/28)
Irradiation of α-bromopropiophenones in the presence of NBS results in the formation of α,β-dibromopropiophenones, which can be viewed as β-bromination of α-bromopropiophenones. The reaction is believed to go through a series of reactions; photoinduced C–Br bond cleavage, elimination of HBr to give α,β-unsaturated ketone intermediates, and addition of Br2, which are formed by the reaction between HBr and NBS. From mechanistic studies of the reaction, we have also found a very convenient method for α-debromination of the α,β-dibromopropiophenones which is by simple irradiation of the dibromo ketones in acetone or 2-propanol without the use of any additives. Our results demonstrate that bromine can be added into or eliminated from the alpha, beta, or both positions to the carbonyl group by photochemical methods, which make synthetic options of bromine containing carbonyl compounds versatile.
49851-31-2 Process route
-

-
C18H22O

-

- 49851-31-2
α-bromovalerophenone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With p-nitrobenzenesulfonamide; hydrogen bromide; oxygen; sodium nitrite; In water; acetonitrile; at 0 - 60 ℃; for 30.5h; under 760.051 Torr;
|
97% |
-

- 583-03-9
1-Phenyl-1-pentanol

-

- 49851-31-2
α-bromovalerophenone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With N-Bromosuccinimide; In tetrahydrofuran; at 20 ℃;
|
49851-31-2 Upstream products
-
1009-14-9

phenyl butyl ketone
-
138042-71-4

2-bromo-1-phenyl-2-(p-tolylsulfinyl)-1-pentanone
-
7726-95-6

bromine
-
64-19-7

acetic acid
49851-31-2 Downstream products
-
107627-04-3

1-phenyl-2-m-tolyloxy-pentan-1-one
-
108622-06-6

2-hydroxy-1-phenyl-pentan-1-one-(methyl-m-tolyl-acetal)
-
101787-92-2

2-hydroxy-1-phenyl-pentan-1-one-(methyl-phenyl-acetal)
-
100134-41-6

4-phenyl-5-propyl-1,3-dihydro-imidazol-2-one
Relevant Products
-
3-BromoanisoleCAS NO.: 2398-37-0
CAS:2398-37-0
-
3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid
CAS:2316-26-9