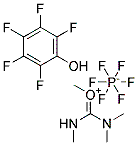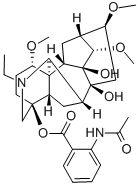
32854-75-4
- Product Name:Lappaconitine
- Molecular Formula:C32H44N2O8
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 32854-75-4
Molecular Formula: C32H44N2O8
Appearance: white powder
|
32854-75-4 Name |
|
|
Name |
Lappaconitine |
|
Synonym |
(1a,14a,16b)-20-Ethyl-1,14,16-trimethoxyaconitane-4,8,9-triol 4-(2-acetylamino)benzoate);(1α,14α,16β)-20-Ethyl-1,14,16-trimethoxyaconitane-;4,8,9-triol4-[2-(acetylamino)benzoate];Aconitane-4,8,9-triol, 20-ethyl-1,14,16-trimethoxy-, 4-(2-acetylamino)benzoate, (1-alpha,14-alpha,16-beta);20-Ethyl-1α,14α,16β-trimethoxyaconitane 4,8,9-triol 4-[2-(acetylamino)benzoate];20-Ethyl-1α,14α,16β-trimethoxyaconitane-4,8,9-triol 4-[2-(acetylamino)benzoate];N-Acetylpuberanidine;Lannaconitine |
|
32854-75-4 Biological Activity |
|
|
Description |
Lappaconitine, isolated from Aconitum sinomontanum Nakai, was characterized as analgesic principle.IC50 value:Target:In vitro: In vivo: Lappaconitine was characterized as analgesic principle by our laboratory. The results suggest that lappaconitine can produce analgesia, possibly through a decrease in cellular calcium availability and PAG may be involved in the Ca2+ antagonistic effect on lappaconitine analgesia [1]. Changes in lappaconitine levels in blood, brain and spinal cord following subcutaneous (s.c.) injection were correlated with the analgesic activity at intervals up to 90 minutes after injection. The equianalgesic doses of lappaconitine (ED50 by the s.c. route and additive ED50 by the i.c.v. plus i.t. route) gave closely similar concentrations of the drug in brain and spinal cord. These results indicate that a simultaneous action of lappaconitine on supraspinal and spinal sites is likely to be important for the analgesia produced by systemically administered lappaconitine [2] |
|
Related Catalog |
Signaling Pathways >> Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel >> P2X Receptor Natural Products >> Alkaloid Research Areas >> Others |
|
References |
[1]. Guo X, et al.Effects of central Ca2+ on analgesic action of lappaconitine. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1989 Nov;10(6):504-7. [2]. Ono M, et al. Pharmacological studies of lappaconitine: supraspinal-spinal interaction in antinociception. Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie [1991, 309:32-41] [3]. Heubach JF, et al. Cardiac effects of lappaconitine and N-deacetyllappaconitine, two diterpenoid alkaloids from plants of the Aconitum and Delphinium species. Planta Med. 1998 Feb;64(1):22-6. |
|
32854-75-4 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
217-218ºC |
|
Boiling point |
720.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C32H44N2O8 |
|
Molecular Weight |
584.700 |
|
Flash Point |
389.7±32.9 °C |
|
PSA |
126.79000 |
|
LogP |
2.13 |
|
Exact Mass |
584.309753 |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.624 |
|
32854-75-4 Description |
|
A highly toxic aconitine alkaloid present in Aconitum leucostomum and A. septentrionale Koelle, lappaconitine crystallizes in hexagonal tablets for whichtwo melting points have been recorded. It has [α]D + 22.3° (C6H6) or [α]18D + 27.0° (CHC1 3). The early view that a methylimino group is present has been shown to be erroneous. No crystalline salts are known but the diacetyl derivative forms colourless crystals, m.p. l25-7°C. The base is only sparingly soluble in H20 and most organic solvents, but dissolves readily in CHC1 3. Boiling the alkaloid with dilute H2S04 in a stream of H2 yields acetic acid and anthranoyllappaconine, C30H4207N2, which forms colourless rhombic tablets, m.p. 146-9°C;[α]25D + 22.07° (C6H6), giving a platinichloride tetrahydrate as brown needles, m.p. 300-31 O°C (dec.). When hydrolyzed with HCl, the base furnishes acetic and anthranilic acids and lappaconine, m.p. 96°C; [α]25D + 22.41°, giving a crystalline hydrochloride, m.p. 246-7°C and the aurichloride monohydrate, m.p. l26-7°C. Alkaline hydrolysis, on the other hand, furnishes lappaconine and lappaconitic acid (acetylanthranilic acid). From these observations, it is clear that only one hydroxyl group is associated with an acyl group in the molecule. Pharmacologically, lappaconitine is toxic although its action is less pronounced than that of aconitine (q.v.). Toxic doses produce respiratory paralysis and have a direct action upon the heart often terminating in ventricular fibrillation. |
Relevant Products
-
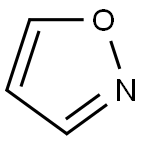
Isoxazole
CAS:288-14-2
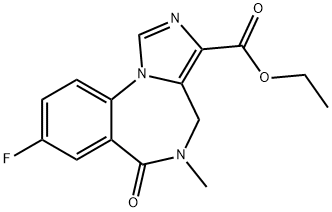
-
Flumazenil
CAS:78755-81-4