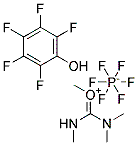
59-92-7
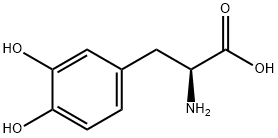
- Product Name:2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoicacid
- Molecular Formula:C9H11NO4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 59-92-7
Molecular Formula: C9H11NO4
Appearance: colorless crystalline powder
|
59-92-7 Name |
|
|
Name |
2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoicacid |
|
Synonym |
2-amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoicacid;3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine(form2);3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine;3,4-DIHYDROXY-L-PHENYLALANINE;3,4-L-DIHYDROXYPHENYLALANINE;3-(3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)-L-ALANINE;3-HYDROXY-L-TYROSINE;BETA-(3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)-L-ALANINE |
|
59-92-7 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
276-278 °C(lit.) |
|
Boiling point |
448.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C9H11NO4 |
|
Molecular Weight |
197.188 |
|
Flash Point |
225.0±28.7 °C |
|
PSA |
103.78000 |
|
LogP |
-0.22 |
|
Exact Mass |
197.068802 |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.655 |
|
Storage condition |
2-8°C |
|
59-92-7 Description |
|
Levodopa is an amino acid precursor of dopamine with antiparkinsonian properties. Levodopa is a prodrug that is converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase and can cross the blood-brain barrier. When in the brain, levodopa is decarboxylated to dopamine and stimulates the dopaminergic receptors, thereby compensating for the depleted supply of endogenous dopamine seen in Parkinson's disease. To assure that adequate concentrations of levodopa reach the central nervous system, it is administered with carbidopa, a decarboxylase inhibitor that does not cross the blood-brain barrier, thereby diminishing the decarboxylation and inactivation of levodopa in peripheral tissues and increasing the delivery of dopamine to the CNS. |
|
59-92-7 Uses |
|
Levodopa is an immediate precursor of dopamine and product of tyrosine hydroxylase. It derived from vanillin is widely used for treatment of Parkinson’s disease, most often in combination with peripheral decarboxylase inhibitors such as benserazide and carbidopa. |
Relevant Products
-
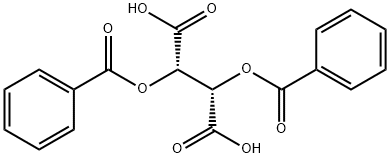
(+)-Dibenzoyl-D-tartaric acid
CAS:17026-42-5
-
Xylazine
CAS:7361-61-7