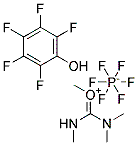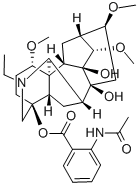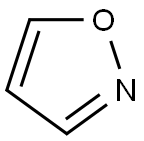
Product Details;
CasNo: 288-14-2
Molecular Formula: C3H3NO
Appearance: colorless liquid
288-14-2 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C3H3NO
- Molecular Weight:69.0629
- Appearance/Colour:colorless liquid
- Vapor Pressure:51.7mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:-67.1°C
- Refractive Index:n20/D 1.427(lit.)
- Boiling Point:95.5 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:-2.0(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:8.9 °C
- PSA:26.03000
- Density:1.055 g/cm3
- LogP:0.67460
288-14-2 Usage
Description
As an important class of heterocycles, isoxazole is a five membered heterocyclic compound with various pharmacological actions, which is found in some natural products, such as ibotenic acid. It is used in the formation of the basis for a number of drugs, such as the COX-2 inhibitor valdecoxib and anti-inflammatory drugs. Isoxazoles are largely applied in the area of pharmaceuticals and therapeutics, including insecticidal, antibacterial, antibiotic, antitumour, antifungal, antituberculosis, anticancer and ulcerogenic. Besides, it has a great effect on reducing blood glucose, eliminating pain, resisting inflammation, killing harmful bacteria, controlling and reducing the risk of HIV. The isoxazole ring is an essential pharmacophore in modern drug discovery. Some beta-lactamase-resistant antibiotics contain an isoxazole group, including cloxacillin, dicloxacillin, flucloxacillin, and the isoxazole group is also found in some steroid drug such as danazol.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isoxazole http://www.ijpcbs.com/files/volume3-2-2013/15.pdf
Chemical Properties
Colorless liquid
Uses
Natural insecticide.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocyclic heteroarene with a structure consisting of a 5-membered ring containing three carbon atoms and an oxygen and nitrogen atom adjacent to each other. It is the parent of the class of isoxazoles.
General Description
Isoxazole are described as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Isoxazole ligands bind to and inhibit the Sxc- antiporter.
Hazard
Narcotic and psychomimetic effects.
InChI:InChI=1/C3H3NO/c1-2-4-5-3-1/h1-3H
288-14-2 Relevant articles
-
Pouchan et al.
, p. 39,40,42,43 (1976)
-
Development of safe and economical synthesis of isoxazole
Nitlikar, Lakshmikant H.,Shinde, Devanand B.
, p. 637 - 639 (2013/12/04)
Isoxazole is a five membered heterocyclic compound having various pharmacological actions. The new practical synthesis of isoxazole from the easily available malonadehyde tetraethyl acetal by avoiding the use of toxic reagent such as cadmium chloride under environment friendly conditions has been developed.
Photocycloaddition of aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes to isoxazoles: Cycloaddition reactivity and stability studies
Griesbeck, Axel G.,Franke, Marco,Neudoerfl, Joerg,Kotaka, Hidehiro
experimental part, p. 127 - 134 (2011/05/16)
The first photocycloadditions of aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes to methylated isoxazoles are reported. The reactions lead solely to the exo-adducts with high regio- and diastereoselectivities. Ring methylation of the isoxazole substrates is crucial for high conversions and product stability. The 6-arylated bicyclic oxetanes 9a-9c were characterized by X-ray structure analyses and showed the highest thermal stabilities. All oxetanes formed from isoxazoles were highly acid-sensitive and also thermally unstable. Cleavage to the original substrates is dominant and the isoxazole derived oxetanes show type T photochromism.
Reactivity of neutral nitrogen donors in square-planar d8 metal complexes: The system chloro(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine)platinum(II) cation with five-membered N-donor heterocycles in methanol
Pitteri, Bruno,Bortoluzzi, Marco
, p. 2698 - 2704 (2008/10/09)
The kinetics of the forward and reverse steps of the reaction [Pt(terpy)Cl]+ + nu ? [Pt(terpy)(nu)]2+ + Cl- (terpy = 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine, nu = one of a number of thiazoles, oxazole, isoxazole, imidazole, pyrazole and 3,5-dimethylpyrazole, covering a wide range of basicities) have been studied in methanol at 25 °C. Both forward and reverse reactions obey the usual two-term rate law observed in square-planar substitution. The second-order rate constants for the forward reactions, k2f, show a slight dependence upon the basicity of the entering nu, while the steric hindrance due to the presence of one methyl group in the α position to the nitrogen markedly decreases the reactivity. The second-order rate constants for the reverse reactions, k2r, are very sensitive to the nature of the leaving group and a plot of log k2r against the pKa of the conjugate acids of the unhindered five-membered N-donors is linear with a slope of -0.51. The results are compared with data from the literature regarding a series of pyridines reacting with the [Pt(terpy)Cl]+ cation under the same experimental conditions. Both in the forward and in the reverse reaction, the reactivity depends not only upon the ligand basicity but also upon the nature of the nucleophile in the order: (thiazoles, oxazole, isoxazole, imidazole, pyrazoles) > pyridines for the entry of N-donors and on the contrary for the displacement by Cl-. Steric retardation, due to the presence of a methyl group in the α position to the nitrogen, is remarkably lower for five-membered N-donors if compared to pyridines both in the forward and in the reverse reaction.
Phosphate transport inhibitors
-
, (2008/06/13)
Disclosed are compounds which have been identified as inhibitors of phosphate transport. Many of the compounds are represented by Structural Formula (I): Ar1—W—X—Y—Ar2; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Ar1 and Ar2 are independently a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group or an optionally substituted five membered or six membered non-aromatic heterocylic group fused to an optionally substituted monocylic aryl group. W and Y are independently a covalent bond or a C1-C3 substituted or unsubstituted alkylene group. X is a heteroatom-containing functional group, an aromatic heterocyclic group, substituted aromatic heterocyclic group, non-aromatic heterocyclic group, substituted non-aromatic heterocyclic group, an olefin group or a substituted olefin group. Also disclosed are methods of treating a subject with a disease associated with hyperphosphatemia, as well as a disease mediated by phosphate-transport function. The methods comprise the step of administering an effective amount of the one of the compounds described above.
288-14-2 Process route

-

- 288-14-2
ISOXAZOLE

-

- 37928-17-9
5-methyl-3,4-diphenyl isoxazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
290 mg (57%) |
-

- 4405-17-8
di(1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)methane

-

- 288-14-2
ISOXAZOLE
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydroxylamine hydrochloride; at 110 - 120 ℃; Green chemistry;
|
85.5% |
288-14-2 Upstream products
-
624-67-9

Propargylic aldehyde
-
5444-80-4

1,3,3-triethoxypropene
-
108-05-4

vinyl acetate
-
15736-98-8

sodium cyanate
288-14-2 Downstream products
-
98020-14-5

4-chloromethyl-isoxazole
-
61310-53-0

3-ethoxyacrylonitrile
-
2032-34-0

3,3-bis(ethyloxy)propanenitrile
-
97925-43-4

4-bromo-1,2-oxazole
Relevant Products
-
E3,Z8,Z11-Tetradecatriene acetate
CAS:163041-94-9