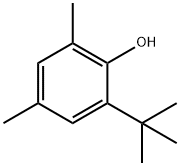
1879-09-0
- Product Name:2-(tert-Butyl)-4,6-dimethylphenol
- Molecular Formula:C12H18O
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 1879-09-0
Molecular Formula: C12H18O
Appearance: yellow liquid
1879-09-0 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C12H18O
- Molecular Weight:178.274
- Appearance/Colour:yellow liquid
- Melting Point:22 ºC
- Refractive Index:1.5183
- Boiling Point:249 ºC at 760 mmHg
- PKA:12.00±0.23(Predicted)
- Flash Point:111.7 ºC
- PSA:20.23000
- Density:0.952 g/cm3
- LogP:3.30650
1879-09-0 Usage
Uses
6-tert-Butyl-2,4-xylenol is an antioxidant found used in rocket and jet fuels.
General Description
A yellow liquid with a phenolic odor. Insoluble in water and about the same density as water. Exposure to skin, eyes or mucous membranes may cause severe burns.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Phenols, such as 2-(tert-Butyl)-4,6-dimethylphenol, do not behave as organic alcohols, as one might guess from the presence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group in their structure. Instead, they react as weak organic acids. Phenols and cresols are much weaker as acids than common carboxylic acids (phenol has Ka = 1.3 x 10^[-10]). These materials are incompatible with strong reducing substances such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Flammable gas (H2) is often generated, and the heat of the reaction may ignite the gas. Heat is also generated by the acid-base reaction between phenols and bases. Such heating may initiate polymerization of the organic compound. Phenols are sulfonated very readily (for example, by concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature). The reactions generate heat. Phenols are also nitrated very rapidly, even by dilute nitric acid. Nitrated phenols often explode when heated. Many of them form metal salts that tend toward detonation by rather mild shock.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
InChI:InChI=1/C15H16Cl3N3O2.C15H24O/c1-2-4-20(15(22)21-5-3-19-10-21)6-7-23-14-12(17)8-11(16)9-13(14)18;1-10-8-11(14(2,3)4)13(16)12(9-10)15(5,6)7/h3,5,8-10H,2,4,6-7H2,1H3;8-9,16H,1-7H3
1879-09-0 Relevant articles
-
Stevens
, p. 655,659 (1943)
-
Chemical Kinetics of the Alkylation of Xylenol for the Separation of Their Close-Boiling Isomers from Coal Tar
Cong-Yu, Ke,Lu, Guo-Min,Sun, Wu-Juan,Tang, Xuan,Wei, Ying-Lin,Zhang, Qun-Zheng,Zhang, Xiao-Xia,Zhang, Xun-Li
, p. 1291 - 1299 (2020/12/02)
Abstract: To support the industrial design and process development for the separation of xylenol isomers from coal tar, the present work was focused on 2,4/2,5-xylenol mixture as 2,4-xylenol and 2,5-xylenol have very close boiling points. Specifically, th
Investigating the microwave-accelerated Claisen rearrangement of allyl aryl ethers: Scope of the catalysts, solvents, temperatures, and substrates
Hui, Zi,Jiang, Songwei,Qi, Xiang,Ye, Xiang-Yang,Xie, Tian
supporting information, (2020/05/18)
The microwave-accelerated Claisen rearrangement of allyl aryl ethers was investigated, in order to gain insight into the scope of the catalysts, solvents, temperatures, and substrates. Among the catalysts examined, phosphomolybdic acid (PMA) was found to greatly accelerate the reaction in NMP, at temperatures ranging from 220 to 300 °C. This method was found to be useful for preparing several intermediates previously reported in the literature using precious metal catalysts such as Au(I), Ag(I), and Pt(II). Additionally, substrates bearing bromo and nitro groups on the aryl portion required careful tailoring of the reaction conditions to avoid complex product profiles.
Highly selective conversion of guaiacol to: Tert -butylphenols in supercritical ethanol over a H2WO4 catalyst
Mai, Fuhang,Cui, Kai,Wen, Zhe,Wu, Kai,Yan, Fei,Chen, Mengmeng,Chen, Hong,Li, Yongdan
, p. 2764 - 2771 (2019/02/01)
The conversion of guaiacol is examined at 300 °C in supercritical ethanol over a H2WO4 catalyst. Guaiacol is consumed completely, meanwhile, 16.7% aromatic ethers and 80.0% alkylphenols are obtained. Interestingly, tert-butylphenols are produced mainly with a high selectivity of 71.8%, and the overall selectivity of 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol is as high as 63.7%. The experimental results indicate that catechol and 2-ethoxyphenol are the intermediates. Meanwhile, the WO3 sites play an important role in the conversion of guaiacol and the Br?nsted acid sites on H2WO4 enhance the conversion and favour a high selectivity of the tert-butylphenols. The recycling tests show that the carbon deposition on the catalyst surface, the dehydration and partial reduction of the catalyst itself are responsible for the decay of the H2WO4 catalyst. Finally, the possible reaction pathways proposed involve the transetherification process and the alkylation process during guaiacol conversion.
Phenol o-position alkylation method
-
Paragraph 0045; 0046; 0047; 0048, (2017/08/27)
The invention provides a phenol o-position alkylation method which comprises the following step: in the presence of a catalyst, a phenol substance and an alkylating agent react, wherein the catalyst is an aryl zinc salt generated from a reaction of zinc and a phenol compound; the alkylating agent is olefin; the phenol substance comprises polyphenol such as catechol and hydroquinone, and further comprises one to two alkyl groups, or halide based phenols; the alkyl group is straight-chain or branched paraffin with 1-10 carbons. By adopting the phenol o-position alkylation method, the preparation efficiency is greatly improved, and the conversion rate can be further increased. The invention further provides a method for preparing 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, and a reaction kettle for preparation.
1879-09-0 Process route
-

- 64-17-5
ethanol

-

- 90-05-1
2-methoxy-phenol

-

- 1020-31-1,122983-47-5,881376-69-8
3,5-Di-tert-butylcatechol

-

- 128-39-2
2,6-di-tert-butylphenol

-

- 2934-05-6
2,4-diisopropylphenol

-

- 2078-54-8
2,6-diisopropylphenol

-

- 2934-07-8
2,4,6-triisopropylphenol

-

- 4130-42-1
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol

-

- 2444-28-2
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenol

-

- 87-97-8
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methoxymethylene-phenol

-

- 1138-52-9
3,5-Di-tert-butylphenol

-

- 1879-09-0
2,4-dimethyl-6-tert-butylphenol

-

- 52417-48-8
2-(2',5'-dimethoxyphenyl)propionaldehyde

-

- 17540-75-9
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-sec-butylphenol

-

- 2050-46-6
1,2-diethoxybenzene

-

- 21112-37-8
1,4-dimethoxy-2-tert-butylbenzene

-

- 5076-72-2
1-ethoxy-4-methoxybenzene

-

- 79-74-3
2,5-di(tert-amyl)-1,4-hydroquinone

-

- 120-95-6
2,4-di-tert-amylphenol

-

- 876-20-0
2,5-diethyl phenol

-

- 33963-27-8
4-ethoxy-3-methoxytoluene

-

- 59056-76-7
1,2-dimethoxy-4-butylbenzene

-

- 131358-04-8
1,2-diethoxy-4-ethyl-benzene

-

- 1620-98-0
3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With ortho-tungstic acid; at 300 ℃; for 6h; Autoclave;
|
-

- 64-17-5
ethanol

-

- 90-05-1
2-methoxy-phenol

-

- 94-71-3
2-Ethoxyphenol

-

- 1020-31-1,122983-47-5,881376-69-8
3,5-Di-tert-butylcatechol

-

- 2934-05-6
2,4-diisopropylphenol

-

- 2078-54-8
2,6-diisopropylphenol

-

- 2934-07-8
2,4,6-triisopropylphenol

-

- 4130-42-1
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-ethylphenol

-

- 2444-28-2
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenol

-

- 87-97-8
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methoxymethylene-phenol

-

- 1138-52-9
3,5-Di-tert-butylphenol

-

- 1879-09-0
2,4-dimethyl-6-tert-butylphenol

-

- 52417-48-8
2-(2',5'-dimethoxyphenyl)propionaldehyde

-

- 17540-75-9
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-sec-butylphenol

-

- 2050-46-6
1,2-diethoxybenzene

-

- 21112-37-8
1,4-dimethoxy-2-tert-butylbenzene

-

- 5076-72-2
1-ethoxy-4-methoxybenzene

-

- 79-74-3
2,5-di(tert-amyl)-1,4-hydroquinone

-

- 120-95-6
2,4-di-tert-amylphenol

-

- 876-20-0
2,5-diethyl phenol

-

- 33963-27-8
4-ethoxy-3-methoxytoluene

-

- 59056-76-7
1,2-dimethoxy-4-butylbenzene

-

- 131358-04-8
1,2-diethoxy-4-ethyl-benzene

-

- 1620-98-0
3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With tungsten(VI) oxide; at 300 ℃; for 6h; Reagent/catalyst; Autoclave;
|
1879-09-0 Upstream products
-
17696-37-6

2,5-dimethyl-4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-phenol
-
105-67-9

2,4-Xylenol
-
115-11-7

isobutene
-
75-65-0

tert-butyl alcohol
1879-09-0 Downstream products
-
136613-00-8

2-t-butyl-4-t-butylperoxy-4,6-dimethyl-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-one
-
147120-00-1

2,2'-di-tert-butyl-6,6'-dimethyl-4,4'-ethanediylidene-bis-cyclohexa-2,5-dienone
-
23500-79-0

2,6-di-methyl-4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxybenzyl chloride
-
105-67-9

2,4-Xylenol
Relevant Products
-
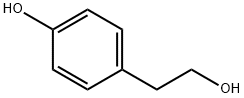
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
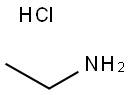
Ethanamine,hydrochloride (1:1)
CAS:557-66-4