872-50-4
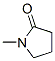
- Product Name:1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone
- Molecular Formula:C5H9NO
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 872-50-4
Molecular Formula: C5H9NO
Appearance: colourless or light yellow liquid with an amine odour
872-50-4 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C5H9NO
- Molecular Weight:99.1326
- Appearance/Colour:colourless or light yellow liquid with an amine odour
- Vapor Pressure:0.29 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
- Melting Point:-24 °C
- Refractive Index:n20/D 1.479
- Boiling Point:201.999 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:-0.41±0.20(Predicted)
- Flash Point:86.111 °C
- PSA:20.31000
- Density:1.033
- LogP:0.17650
872-50-4 Usage
Chemical Properties
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a colorless to light yellow transparent liquid with a slight ammonia odor. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is completely miscible with water. It is highly soluble in lower alcohols, lower ketones, ether, ethyl acetate, chloroform, and benzene and moderately soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is strongly hygroscopic, chemically stable, not corrosive towards carbon steel and aluminum, and slightly corrosive to copper. It has low adhesiveness, strong chemical and thermal stability, high polarity, and low volatility. This product is slightly toxic, and its permitted concentration limit in air is 100ppm.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is a solvent used in a variety of industries and applications, such as paint and coating removal, petrochemical processing, engineering plastics coatings, agricultural chemicals, electronic cleaning and industrial/domestic cleaning.
Uses
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) is a polar aprotic solvent that has the advantages of low toxicity, high boiling point, outstanding solvency, strong selectivity and good stability. It is widely used in purification of aromatic hydrocarbon extraction, acetylene, olefins, and diolefins.It is used in industrial cleaning, and it serves as a solvent for production of pesticides, engineering plastics, coatings, synthetic fibers, and integrated circuits.It can also be used as an industrial cleanser, dispersant, dye, lubricant and antifreeze.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is an excellent solvent, widely used in aromatics extraction, lubricating oil refining, acetylene enrichment, butadiene separation and synthesis gas desulfurization.It is used in gas desulfurization, lubricating oil refining, lubricating oil antifreeze, olefin extraction, and as a solvent for insoluble engineering plastics polymerization.It can be used in herbicide, to clean insulation materials, semiconductor industry precision instruments and circuit boards, to recycle PVC exhaust, as a detergent, dye supplement and dispersing agent.It is used in mediums for polymerization reactions such as engineering plastics and aramid fiber.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is used as a polyvinylidene fluoride solvent and electrode auxiliary material for lithium ion batteries.high purity grade for ICP-MS detection.For peptide synthesis.
toxicity
Oral (mus)LD50:5130 mg/kg;Oral (rat)LD50:3914 mg/kg;Dermal (rbt)LD50:8000 mg/kg.
Waste Disposal
Consult state, local or national regulations for proper disposal. Disposal must be made according to official regulations. Water, if necessary with cleansing agents.
storage
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is hygroscopic (picks up moisture) but stable under normal conditions. It will violently react with strong oxidizers such as hydrogen peroxide, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, etc. The primary decomposition products produce carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide fumes. Excessive exposure or spillage should be avoided as a matter of good practice. Lyondell Chemical Company recommends wearing butyl gloves when using N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?should be stored in clean, phenolic-lined mild steel or alloy drums. Teflon?1 and Kalrez?1 have been shown to be suitable gasket materials. Please review MSDS prior to handling.
Description
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is an aprotic solvent with a wide range of applications: petrochemical processing, surface coating, dyes and pigments, industrial and domestic cleaning compounds, and agricultural and pharmaceutical formulations. It is mainly an irritant, but has also caused several cases of contact dermatitis in a small electrotechnical company.
Chemical Properties
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a colourless or light yellow liquid with an amine odour. It can undergo a number of chemical reactions even though it is accepted as a stable solvent. It is resistant to hydrolysis under neutral conditions, but strong acid or base treatment results in ring opening to 4-methyl aminobutyric acid. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?can be reduced to 1-methyl pyrrolidine with borohydride. Treatment with chlorinating agents results in amide formation,an intermediate which can undergo further substitution, while treatment with amyl nitrate yields the nitrate. Olefins can be added to the 3 position by treatment first with oxalic esters, then with appropriate aldehyes (Hort and Anderson 1982).
Uses
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a polar solvent that is used in organic chemistry and polymer chemistry. Large scale applications include the recovery and purification of acetylenes, olefins, and diolefins, gas purification, and aromatics extraction from feedstocks.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a versatile industrial solvent. NMP is currently approved for use only in veterinary pharmaceuticals. The determination of the disposition and metabolism of NMP in the rat will contribute toward understanding the toxicology of this exogenous chemical which man may likely be exposed to in increasing amounts.
Uses
Solvent for high-temperature resins; petrochemical processing, in the microelectronics fabrication industry, dyes and pigments, industrial and domestic cleaning compounds; agricultural and pharmaceutical formulations
Uses
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone, is useful for spectrophotometry, chromatography and ICP-MS detection.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of pyrrolidine-2-ones that is pyrrolidin-2-one in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a methyl group.
Production Methods
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is manufactured by the reaction of buytrolactone with methylamine (Hawley 1977). Other processes include preparation by hydrogenation of solutions of maleic or succinic acids with methylamine (Hort and Anderson 1982). Manufacturers of this chemical include Lachat Chemical, Inc, Mequon, Wisconsin and GAF Corporation, Covert City, California.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 24, p. 1323, 1983 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)81646-9
General Description
N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone (NMP) is a powerful, aprotic solvent with high solvency, and low volatility. This colorless, high boiling, high flash point and low vapor pressure liquid carries a mild amine-like odor. NMP has high chemical and thermal stability and is completely miscible with water at all temperatures. NMP can serve as a co-solvent with water, alcohols, glycol ethers, ketones, and aromatic/chlorinated hydrocarbons. NMP is both recyclable by distillation and readily biodegradable. NMP is not found on the Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs) list of the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
This amine is a very mild chemical base. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone does tend to neutralize acids to form salts plus water. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Hazard
Severe skin and eye irritant. Explosive lim-its 2.2–12.2%.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of hot vapors can irritate nose and throat. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Contact with eyes causes irritation. Repeated and prolonged skin contact produces a mild, transient irritation.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic oxides of nitrogen may be formed in fire.
Flammability and Explosibility
Nonflammable
Industrial uses
1) N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is used as a general dipolar aprotic solvent, stable and unreactive;2) for extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from lubricating oils;3) for carbon dioxide removal in ammonia generators;4) as a solvent for polymerization reactions and polymers;5) as a paint stripper;6) for pesticide formulations (USEPA 1985).Other non-industrial uses of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?are based on its properties as a dissociating solvent suitable for electrochemical and physical chemical studies (Langan and Salman 1987). Pharmaceutical applications make use of the properties of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?as a penetration enhancer for a more rapid transfer of substances through the skin (Kydoniieus 1987; Barry and Bennett 1987; Akhter and Barry 1987). N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?has been approved as a solvent for slimicide application to food packaging materials (USDA 1986).
Contact allergens
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is an aprotic solvent with a wide range of applications: petrochemical processing, surface coating, dyes and pigments, industrial and domestic cleaning compounds, and agricultural and pharmaceutical formulations. It is mainly an irritant, but it can cause severe contact dermatitis due to prolonged contact.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by skin contact. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Combustible when exposed to heat, open flame, or powerful oxidizers. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Carcinogenicity
Rats were exposed to N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?vapor at 0, 0.04, or 0.4 mg/L for 6 h/day, 5 days/week for 2 years.Male rats at 0.4 mg/L showed slightly reduced mean body weight. No life-shortening toxic or carcinogenic effects were observed in rats exposed for 2 years to either 0.04 or 0.4mg/L of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone. By the dermal route, a group of 32 mice received an initiation dose of 25mg of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?followed 2 weeks later by applications of the tumor promoter phorbol myristate acetate, three times a week, for more than 25 weeks. Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride and dimethylbenzanthracene served as positive controls. Although the N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?group had three skin tumors, this response was not considered significant when compared with that of the positive controls.
Metabolic pathway
Rats are administered radio-labeled N-methyl-2- pyrrolidinone (NMP), and the major route of excretion by rats is via the urine. The major metabolite, representing 70-75% of the administered dose, is 4-(methylamino)butenoic acid. This unsaturated intact product may be formed from the elimination of water, and a hydroxyl group may be present on the metabolite prior to acid hydrolysis.
Metabolism
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were given a single intraperitoneal injection (45 mg/kg) of radiolabeled 1 -methyl-2-pyrrolidone. Plasma levels of radioactivity and compound were monitored for six hours and the results suggested a rapid distribution phase which was followed by a slow elimination phase. The major amount of label was excreted in the urine within 12 hours and accounted for approximately 75% of the labelled dose. Twenty-four hours after dosage, cumulative excretion (urine) was approximately 80% of the dose. Both ring- and methyl-labeled species were used, as well as both [14C]- and [3H]-labeled l-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. The initial labeled ratios were maintained during the first 6 hours after dosage. After 6 hours, the liver and intestines were found to contain the highest accumulations of radioactivity, approximately 2-4% of the dose. Little radioactivity was noted in the bile or respired air. High performance liquid chromatography of urine showed the presence of one major and two minor metabolites. The major metabolite (70-75% of the administered radioactive dose) was analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and was proposed to be a 3- or 5-hydroxy-l-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (Wells 1987).
Purification Methods
Dry the pyrrolidone by removing water as the *benzene azeotrope. Fractionally distil at 10 torr through a 100-cm column packed with glass helices. [Adelman J Org Chem 29 1837 1964, McElvain & Vozza J Am Chem Soc 71 896 1949.] The hydrochloride has m 86-88o (from EtOH or Me2CO/EtOH) [Reppe et al. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 596 1 1955]. [Beilstein 21 II 213, 21 III/IV 3145, 21/6 V 321.]
Chemical Properties
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a colorless to light yellow transparent liquid with a slight ammonia odor. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is completely miscible with water. It is highly soluble in lower alcohols, lower ketones, ether, ethyl acetate, chloroform, and benzene and moderately soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is strongly hygroscopic, chemically stable, not corrosive towards carbon steel and aluminum, and slightly corrosive to copper. It has low adhesiveness, strong chemical and thermal stability, high polarity, and low volatility. This product is slightly toxic, and its permitted concentration limit in air is 100ppm.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is a solvent used in a variety of industries and applications, such as paint and coating removal, petrochemical processing, engineering plastics coatings, agricultural chemicals, electronic cleaning and industrial/domestic cleaning.
Uses
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) is a polar aprotic solvent that has the advantages of low toxicity, high boiling point, outstanding solvency, strong selectivity and good stability. It is widely used in purification of aromatic hydrocarbon extraction, acetylene, olefins, and diolefins.It is used in industrial cleaning, and it serves as a solvent for production of pesticides, engineering plastics, coatings, synthetic fibers, and integrated circuits.It can also be used as an industrial cleanser, dispersant, dye, lubricant and antifreeze.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is an excellent solvent, widely used in aromatics extraction, lubricating oil refining, acetylene enrichment, butadiene separation and synthesis gas desulfurization.It is used in gas desulfurization, lubricating oil refining, lubricating oil antifreeze, olefin extraction, and as a solvent for insoluble engineering plastics polymerization.It can be used in herbicide, to clean insulation materials, semiconductor industry precision instruments and circuit boards, to recycle PVC exhaust, as a detergent, dye supplement and dispersing agent.It is used in mediums for polymerization reactions such as engineering plastics and aramid fiber.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is used as a polyvinylidene fluoride solvent and electrode auxiliary material for lithium ion batteries.high purity grade for ICP-MS detection.For peptide synthesis.
toxicity
Oral (mus)LD50:5130 mg/kg;Oral (rat)LD50:3914 mg/kg;Dermal (rbt)LD50:8000 mg/kg.
Waste Disposal
Consult state, local or national regulations for proper disposal. Disposal must be made according to official regulations. Water, if necessary with cleansing agents.
storage
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is hygroscopic (picks up moisture) but stable under normal conditions. It will violently react with strong oxidizers such as hydrogen peroxide, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, etc. The primary decomposition products produce carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide fumes. Excessive exposure or spillage should be avoided as a matter of good practice. Lyondell Chemical Company recommends wearing butyl gloves when using N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?should be stored in clean, phenolic-lined mild steel or alloy drums. Teflon?1 and Kalrez?1 have been shown to be suitable gasket materials. Please review MSDS prior to handling.
Description
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is an aprotic solvent with a wide range of applications: petrochemical processing, surface coating, dyes and pigments, industrial and domestic cleaning compounds, and agricultural and pharmaceutical formulations. It is mainly an irritant, but has also caused several cases of contact dermatitis in a small electrotechnical company.
Chemical Properties
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a colourless or light yellow liquid with an amine odour. It can undergo a number of chemical reactions even though it is accepted as a stable solvent. It is resistant to hydrolysis under neutral conditions, but strong acid or base treatment results in ring opening to 4-methyl aminobutyric acid. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?can be reduced to 1-methyl pyrrolidine with borohydride. Treatment with chlorinating agents results in amide formation,an intermediate which can undergo further substitution, while treatment with amyl nitrate yields the nitrate. Olefins can be added to the 3 position by treatment first with oxalic esters, then with appropriate aldehyes (Hort and Anderson 1982).
Uses
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a polar solvent that is used in organic chemistry and polymer chemistry. Large scale applications include the recovery and purification of acetylenes, olefins, and diolefins, gas purification, and aromatics extraction from feedstocks.N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is a versatile industrial solvent. NMP is currently approved for use only in veterinary pharmaceuticals. The determination of the disposition and metabolism of NMP in the rat will contribute toward understanding the toxicology of this exogenous chemical which man may likely be exposed to in increasing amounts.
Uses
Solvent for high-temperature resins; petrochemical processing, in the microelectronics fabrication industry, dyes and pigments, industrial and domestic cleaning compounds; agricultural and pharmaceutical formulations
Uses
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone, is useful for spectrophotometry, chromatography and ICP-MS detection.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of pyrrolidine-2-ones that is pyrrolidin-2-one in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a methyl group.
Production Methods
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is manufactured by the reaction of buytrolactone with methylamine (Hawley 1977). Other processes include preparation by hydrogenation of solutions of maleic or succinic acids with methylamine (Hort and Anderson 1982). Manufacturers of this chemical include Lachat Chemical, Inc, Mequon, Wisconsin and GAF Corporation, Covert City, California.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 24, p. 1323, 1983 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)81646-9
General Description
N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone (NMP) is a powerful, aprotic solvent with high solvency, and low volatility. This colorless, high boiling, high flash point and low vapor pressure liquid carries a mild amine-like odor. NMP has high chemical and thermal stability and is completely miscible with water at all temperatures. NMP can serve as a co-solvent with water, alcohols, glycol ethers, ketones, and aromatic/chlorinated hydrocarbons. NMP is both recyclable by distillation and readily biodegradable. NMP is not found on the Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs) list of the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
This amine is a very mild chemical base. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone does tend to neutralize acids to form salts plus water. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Hazard
Severe skin and eye irritant. Explosive lim-its 2.2–12.2%.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of hot vapors can irritate nose and throat. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Contact with eyes causes irritation. Repeated and prolonged skin contact produces a mild, transient irritation.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic oxides of nitrogen may be formed in fire.
Flammability and Explosibility
Nonflammable
Industrial uses
1) N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?is used as a general dipolar aprotic solvent, stable and unreactive;2) for extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from lubricating oils;3) for carbon dioxide removal in ammonia generators;4) as a solvent for polymerization reactions and polymers;5) as a paint stripper;6) for pesticide formulations (USEPA 1985).Other non-industrial uses of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?are based on its properties as a dissociating solvent suitable for electrochemical and physical chemical studies (Langan and Salman 1987). Pharmaceutical applications make use of the properties of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?as a penetration enhancer for a more rapid transfer of substances through the skin (Kydoniieus 1987; Barry and Bennett 1987; Akhter and Barry 1987). N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?has been approved as a solvent for slimicide application to food packaging materials (USDA 1986).
Contact allergens
N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone is an aprotic solvent with a wide range of applications: petrochemical processing, surface coating, dyes and pigments, industrial and domestic cleaning compounds, and agricultural and pharmaceutical formulations. It is mainly an irritant, but it can cause severe contact dermatitis due to prolonged contact.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by skin contact. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Combustible when exposed to heat, open flame, or powerful oxidizers. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Carcinogenicity
Rats were exposed to N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?vapor at 0, 0.04, or 0.4 mg/L for 6 h/day, 5 days/week for 2 years.Male rats at 0.4 mg/L showed slightly reduced mean body weight. No life-shortening toxic or carcinogenic effects were observed in rats exposed for 2 years to either 0.04 or 0.4mg/L of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone. By the dermal route, a group of 32 mice received an initiation dose of 25mg of N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?followed 2 weeks later by applications of the tumor promoter phorbol myristate acetate, three times a week, for more than 25 weeks. Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride and dimethylbenzanthracene served as positive controls. Although the N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone?group had three skin tumors, this response was not considered significant when compared with that of the positive controls.
Metabolic pathway
Rats are administered radio-labeled N-methyl-2- pyrrolidinone (NMP), and the major route of excretion by rats is via the urine. The major metabolite, representing 70-75% of the administered dose, is 4-(methylamino)butenoic acid. This unsaturated intact product may be formed from the elimination of water, and a hydroxyl group may be present on the metabolite prior to acid hydrolysis.
Metabolism
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were given a single intraperitoneal injection (45 mg/kg) of radiolabeled 1 -methyl-2-pyrrolidone. Plasma levels of radioactivity and compound were monitored for six hours and the results suggested a rapid distribution phase which was followed by a slow elimination phase. The major amount of label was excreted in the urine within 12 hours and accounted for approximately 75% of the labelled dose. Twenty-four hours after dosage, cumulative excretion (urine) was approximately 80% of the dose. Both ring- and methyl-labeled species were used, as well as both [14C]- and [3H]-labeled l-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. The initial labeled ratios were maintained during the first 6 hours after dosage. After 6 hours, the liver and intestines were found to contain the highest accumulations of radioactivity, approximately 2-4% of the dose. Little radioactivity was noted in the bile or respired air. High performance liquid chromatography of urine showed the presence of one major and two minor metabolites. The major metabolite (70-75% of the administered radioactive dose) was analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and was proposed to be a 3- or 5-hydroxy-l-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (Wells 1987).
Purification Methods
Dry the pyrrolidone by removing water as the *benzene azeotrope. Fractionally distil at 10 torr through a 100-cm column packed with glass helices. [Adelman J Org Chem 29 1837 1964, McElvain & Vozza J Am Chem Soc 71 896 1949.] The hydrochloride has m 86-88o (from EtOH or Me2CO/EtOH) [Reppe et al. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 596 1 1955]. [Beilstein 21 II 213, 21 III/IV 3145, 21/6 V 321.]
InChI:InChI=1/C5H9NO/c1-6-4-2-3-5(6)7/h2-4H2,1H3
872-50-4 Relevant articles
Preparation of alkylated compounds using the trialkylphosphate
-
Paragraph 0184-0185; 0210, (2021/11/02)
[Problem] trialkylphosphate strong base used reaction agent, a carboxylic acid, a ketone, an aldehyde, amine, amide, thiol, ester or Grignard reagent to a variety of substrates, and/or high efficiency to generate a highly stereoselective alkylation reaction, the alkylated compounds capable of producing new means. [Solution] was used as the alkylating agent in the alkylation of compound trialkylphosphate, strongly basic reaction production use. [Drawing] no
Regio- And Stereoselective (S N2) N -, O -, C - And S -Alkylation Using Trialkyl Phosphates
Banerjee, Amit,Hattori, Tomohiro,Yamamoto, Hisashi
, (2021/06/16)
Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (S N 2) is one of the most well-known fundamental reactions in organic chemistry to generate new molecules from two molecules. In principle, a nucleophile attacks from the back side of an alkylating agent having a suitable leaving group, most commonly a halide. However, alkyl halides are expensive, very harmful, toxic and not so stable, which makes them problematic for laboratory use. In contrast, trialkyl phosphates are inexpensive, readily accessible and stable at room temperature, under air, and are easy to handle, but rarely used as alkylating agents in organic synthesis. Here, we describe a mild, straightforward and powerful method for nucleophilic alkylation of various N -, O -, C - and S -nucleophiles using readily available trialkyl phosphates. The reaction proceeds smoothly in excellent yield, and quantitative yield in many cases, and covers a wide range of substrates. Further, the rare stereoselective transfer of secondary alkyl groups has been achieved with inversion of configuration of chiral centers (up to 98% ee).
Rapid and Mild Lactamization Using Highly Electrophilic Triphosgene in a Microflow Reactor
Fuse, Shinichiro,Komuro, Keiji,Otake, Yuma,Masui, Hisashi,Nakamura, Hiroyuki
supporting information, p. 7525 - 7532 (2021/03/17)
Lactams are cyclic amides that are indispensable as drugs and as drug candidates. Conventional lactamization includes acid-mediated and coupling-agent-mediated approaches that suffer from narrow substrate scope, much waste, and/or high cost. Inexpensive, less-wasteful approaches mediated by highly electrophilic reagents are attractive, but there is an imminent risk of side reactions. Herein, a methods using highly electrophilic triphosgene in a microflow reactor that accomplishes rapid (0.5–10 s), mild, inexpensive, and less-wasteful lactamization are described. Methods A and B, which use N-methylmorpholine and N-methylimidazole, respectively, were developed. Various lactams and a cyclic peptide containing acid- and/or heat-labile functional groups were synthesized in good to high yields without the need for tedious purification. Undesired reactions were successfully suppressed, and the risk of handling triphosgene was minimized by the use of microflow technology.
Triazinetriamine-derived porous organic polymer-supported copper nanoparticles (Cu-NPs@TzTa-POP): an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of: N -methylated products via CO2fixation and primary carbamates from alcohols and urea
Haque, Najirul,Biswas, Surajit,Basu, Priyanka,Haque Biswas, Imdadul,Khatun, Resmin,Khan, Aslam,Islam, Sk Manirul
supporting information, p. 15446 - 15458 (2020/10/22)
In recent times, carbon dioxide fixation has received much attention for its potential application as an abundant C1 source and a range of important fine chemicals can be manufactured via this fixation. Here, a copper nanoparticle-decorated porous organic polymer-based (Cu-NPs@TzTa-POP) material was prepared by a simple in situ process. The catalyst was characterized by various techniques such as UV-vis spectra, FTIR spectra, HR-TEM, PXRD, N2 adsorption-desorption, TG-DTA, XPS, and AAS analysis. The synthesized heterogeneous catalyst showed excellent activity in an atmospheric carbon dioxide fixation reaction to produce N-methylated products from aromatic/heterocyclic amines in the presence of polymethyl-hydrosiloxane (PMHS) as the reducing agent at 80 °C within 12 h of the reaction. Through this catalytic N-methylation reaction, we obtained 98% yield of the product with turnover frequency ranging from 18 to 42 h-1. The catalyst is also very stable for the formation of primary carbamates from alcohols using the eco-friendly carbonylating agent, urea. Diverse alcohols (such as benzylic alcohols, phenols, heterocyclic alcohols, as well as aliphatic alcohols) showed much acceptance to this catalytic reaction and produced moderate to excellent yields of the respective carbamate products under ambient reaction conditions. Moreover, Cu-NPs@TzTa-POP is effortlessly recyclable and reusable without the extensive loss of active copper metal centres for many catalytic rounds (up to six catalytic rounds were examined).
872-50-4 Process route
-

- 616-45-5
2-pyrrolidinon

-

- 67-56-1
methanol

-

- 96-48-0
4-butanolide

-

- 872-50-4,26138-58-9
1-methyl-pyrrolidin-2-one

-

- 591-81-1
4-hydroxybutanoic acid

-

- 925-57-5
methyl 4-hydroxybutanoate

-

- 64-20-0
tetramethylammonium bromide

-

- 75-50-3
trimethylamine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With ammonium bromide; at 250 ℃; for 5.33333h; under 3750.38 Torr; Inert atmosphere; Autoclave;
|
-

- 120-94-5
1-Methylpyrrolidine

-

- 123-75-1
pyrrolidine

-

- 872-50-4,26138-58-9
1-methyl-pyrrolidin-2-one

-

- 50-00-0,30525-89-4,61233-19-0
formaldehyd

-

- 1119-48-8
4-(methylamino)butyric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With (batho)2CuII (batho = 2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthrolinedisulfonate); water; at 25 ℃; for 24h; Rate constant; Product distribution; Mechanism; pH 8; var. reaction time and amine concentration; other aliphatic amines;
|
872-50-4 Upstream products
-
186581-53-3

diazomethane
-
626-64-2

pyridin-4-ol
-
60-29-7

diethyl ether
-
616-45-5

2-pyrrolidinon
872-50-4 Downstream products
-
72311-87-6

3-(α-hydroxy-benzhydryl)-1-methyl-pyrrolidin-2-one
-
454-14-8

cuscohygrine
-
97706-81-5

(3-methyl-3H-benzothiazol-2-ylidenehydrazono)-phenyl-acetonitrile
-
765-48-0

1,2-dimethylpyrrolidine
Relevant Products
-
Pregabalin
CAS:148553-50-8
-
Triethoxyoctylsilane
CAS:2943-75-1