125248-71-7
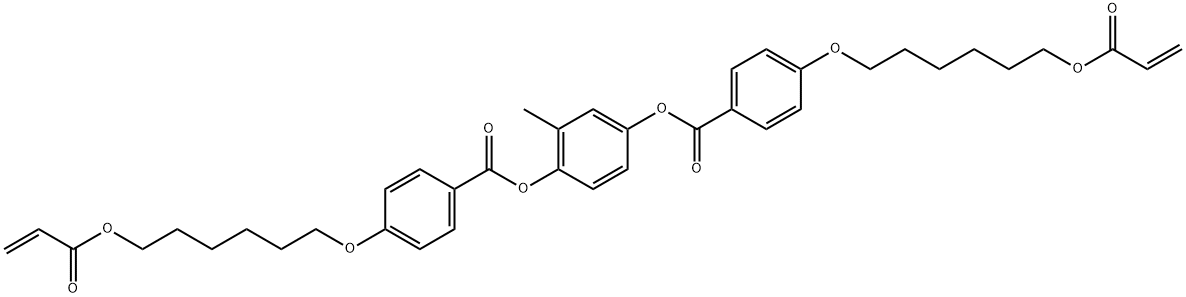
- Product Name:1,4-Bis-[4-(6-acryloyloxyhexyloxy)benzoyloxy]-2-methylbenzene
- Molecular Formula:C39H44O10
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 125248-71-7
Molecular Formula: C39H44O10
125248-71-7 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C39H44O10
- Molecular Weight:672.772
- Vapor Pressure:3.19E-24mmHg at 25°C
- Refractive Index:1.548
- Boiling Point:779.2 °C at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:314.5 °C
- PSA:114.43000
- Density:1.156 g/cm3
- LogP:7.93390
125248-71-7 Usage
Chemical Properties
White powder
InChI:InChI=1/C39H44O10/c1-4-36(40)46-26-12-8-6-10-24-44-32-18-14-30(15-19-32)38(42)48-34-22-23-35(29(3)28-34)49-39(43)31-16-20-33(21-17-31)45-25-11-7-9-13-27-47-37(41)5-2/h4-5,14-23,28H,1-2,6-13,24-27H2,3H3
125248-71-7 Relevant articles
Constructing stable ordered ion channels for a solid electrolyte membrane with high ionic conductivity by combining the advantages of liquid crystal and ionic liquid
Wang, Shi,Zeng, Qinghui,Wang, Ailian,Liu, Xu,Chen, Jie,Wang, Zhinan,Zhang, Liaoyun
, p. 1069 - 1075 (2019)
The advantages of solid-state polymer electrolytes (SPEs) such as ease of fabrication, high safety, good compatibility with Li metals make SPEs one of the most promising electrolyte materials for next generation high-performance and high-safety lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). However, the traditionally used PEO-based electrolytes usually exhibit very low ionic conductivity due to the high crystallinity of PEO, which impedes the commercialization of solid-state LIBs using PEO-based polymer electrolytes. In this study, an 'alternative' solid electrolyte material was prepared using a nematic liquid crystal (LC) and an ionic liquid (IL). Specifically, the LC with ordered layered nanostructures was polymerized and immobilized via UV-irradiation, while IL was sufficiently inserted into the ordered ion channels for fast transport ions. It should be noted that such a free-standing electrolyte film with stable ordered channels has been confirmed through the characterizations of DSC, POM, SEM and XRD. As a result, the solid electrolyte film shows superior comprehensive electrochemical performance in terms of a very high room temperature ionic conductivity (2.14 × 10-2 S cm-1), wide electrochemical window (4.8 V), and very good compatibility with lithium metal. Furthermore, the LiFePO4/Li cell using the ordered electrolyte film shows an average discharge capacity of 150 mA h g-1. Undoubtedly, our study provides a new solid electrolyte material that has the potential to be used in the next generation of high safety and high energy density LIBs.
Broadband reflection of polymer-stabilized chiral nematic liquid crystals induced by a chiral azobenzene compound
Chen, Xingwu,Wang, Ling,Chen, Yinjie,Li, Chenyue,Hou, Guoyan,Liu, Xin,Zhang, Xiaoguang,He, Wanli,Yang, Huai
supporting information, p. 691 - 694 (2014/01/06)
A chiral nematic liquid crystal-photopolymerizable monomer-chiral azobenzene compound composite was prepared and then polymerized under UV irradiation. The reflection wavelength of the composite can be extended to cover the 1000-2400 nm range and also be adjusted to the visible light region by controlling the concentration of chiral compounds.
POLYMERIZABLE COMPOUND AND COMPOSITION CONTAINING THE POLYMERIZABLE COMPOUND
-
Page/Page column 37-38, (2010/11/28)
The polymerizable compound of the present invention is represented by general formula (1) below and can provide a composition that is polymerizable near ambient temperature and exists in a liquid crystal phase at low temperatures. The composition and a (co)polymer of the polymerizable compound of the present invention are liquid crystal substances useful as optically anisotropic materials. (In the formula, each of rings A1 to A3 represents a benzene ring, cyclohexane ring, etc.; each of X to Z represents a C1-8 alkyl or alkoxy group, C2-6 alkenyl group, halogen atom, cyano group, or CH2=CR3-COO-; each of R1 to R3 represents a hydrogen atom, methyl group, or halogen atom; each of L1 to L3 represents -CH2CH2COO-, -COO-, -OCO-, -CH2CH2-, -O(CH2)f- (herein, f = 1-8), etc.; n represents 0 or 1; and a to c represent such numbers that the polymerizable compound has at least one or more of any of X, Y, and Z.)
125248-71-7 Process route
-

- 95-71-6,96937-50-7
2-methylbenzene-1,4-diol

-
![4-{[6-(acryloyloxy)hexyl]oxy}benzoic acid](/upload/2023/1/30c719e6-6af7-439c-b996-fb07db6ba7ac.png)
- 83883-26-5
4-{[6-(acryloyloxy)hexyl]oxy}benzoic acid

-
![1,4-di-[4-(6-acryloyloxy)hexyloxybenzoyloxy]-2-methylbenzene](/upload/2023/1/1dec4197-b0ec-4ebc-90ed-a7f12a9ec73f.png)
- 125248-71-7
1,4-di-[4-(6-acryloyloxy)hexyloxybenzoyloxy]-2-methylbenzene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With dmap; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide; In dichloromethane; for 48h;
|
70.5% |
|
With dmap; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide; In dichloromethane; at 20 ℃; for 48h;
|
-

- 2009-83-8
6-chloro-1-hexanol

-
![1,4-di-[4-(6-acryloyloxy)hexyloxybenzoyloxy]-2-methylbenzene](/upload/2023/1/1dec4197-b0ec-4ebc-90ed-a7f12a9ec73f.png)
- 125248-71-7
1,4-di-[4-(6-acryloyloxy)hexyloxybenzoyloxy]-2-methylbenzene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Multi-step reaction with 4 steps
1: sodium hydroxide; potassium iodide / acetone / 20 h / 60 °C
2: potassium hydroxide / water / 6 h / 60 °C
3: N,N-dimethyl-aniline / 1,4-dioxane / 3 h / 60 °C
4: dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide; dmap / dichloromethane / 48 h
With dmap; N,N-dimethyl-aniline; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide; potassium iodide; potassium hydroxide; sodium hydroxide; In 1,4-dioxane; dichloromethane; water; acetone;
|
125248-71-7 Upstream products
-
95-71-6

2-methylbenzene-1,4-diol
-
83883-26-5

4-{[6-(acryloyloxy)hexyl]oxy}benzoic acid
-
2009-83-8

6-chloro-1-hexanol
-
120-47-8

Ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
Relevant Products
-
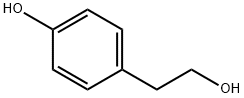
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
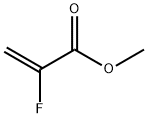
2-Propenoic acid,2-fluoro-, methyl ester
CAS:2343-89-7
-
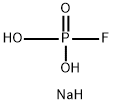
Disodium monofluorophosphate
CAS:10163-15-2