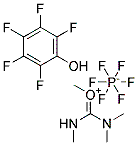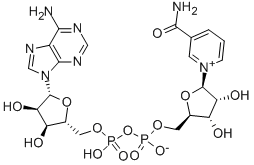
53-84-9
- Product Name:beta-Diphosphopyridine
- Molecular Formula:C21H27N7O14P2
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 53-84-9
Molecular Formula: C21H27N7O14P2
Appearance: White powder
|
53-84-9 Name |
|
|
Name |
beta-Diphosphopyridine nucleotide food grade |
|
Synonym |
OSTEOPONTIN, GST FUSION;)-1-beta-d-ribofuranosylpyridiniumhydroxide,innersalt;adenine-nicotinamidedinucleotide;adenosine5’-(trihydrogendiphosphate),p’.fwdarw.’-esterwith3-(aminocarbonyl;Adenosine5’-(trihydrogendiphosphate),P’.fwdarw.5’-esterwith3-(aminocarbonyl)-1-.beta.-D-ribofuranosylpyridinium,innersalt;beta-diphosphopyridine;cozymasei;enzopride |
|
53-84-9 Biological Activity |
|
|
Description |
NAD+ is a coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-diphosphate coupled to adenosine 5'-phosphate by pyrophosphate linkage. |
|
Related Catalog |
Research Areas >> Metabolic Disease Natural Products >> Saccharides and Glycosides |
|
Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
|
In Vitro |
NAD+ is a coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-diphosphate coupled to adenosine 5'-phosphate by pyrophosphate linkage. NAD+ is the oxidized form of NADH[1]. NAD+ is found widely in nature and is involved in numerous enzymatic reactions in which it serves as an electron carrier by being alternately oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (Nadide) [2]. |
|
In Vivo |
Oral NAD+ supplementation has been used to combat simple fatigue as well as such mysterious and energy-sapping disorders as chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia[3]. |
|
References |
[1]. Viollet, B., et al., Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci (Lond), 2012. 122(6): p. 253-70.[2]. Brandt, U., Energy converting NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (complex I). Annu Rev Biochem, 2006. 75: p. 69-92.[3]. Kussmaul, L. and J. Hirst, The mechanism of superoxide production by NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) from bovine heart mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2006. 103(20): p. 7607-12. |
|
53-84-9 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
140 - 142ºC |
|
Molecular Formula |
C21H27N7O14P2 |
|
Molecular Weight |
663.425 |
|
Form |
Powder |
|
Color |
White |
|
PSA |
340.71000 |
|
LogP |
-5.72 |
|
Exact Mass |
663.109131 |
|
storage temp. |
-20°C |
|
solubility |
H2O: 50 mg/mL |
|
53-84-9 Description |
|
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) plays a major role in metabolism as a cofactor and mobile electron acceptor. NAD+ is a required oxidizing cosubstrate for many enzymes. It is reduced to NADH (Cat# N-035) which carries electrons to the electron transport chain for subsequent oxidative phorphorylation and ATP production. NAD+ is capable of donating ADP-ribose moieties to a protein, producing nicotinamide in the process. Sirtuin enzymes use NAD+ as a substrate to deacetylate proteins and direct activity between the nucleus and mitochondria. NAD+ is regenerated by fermentation and by oxidative phosphorylation. |
|
53-84-9 Uses |
|
β-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide is a coeznyme consisting of an adenine base and a nicotinamide base connected by a pair of bridging phosphate group. β-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide acts as a c oenzyme in redox reactions, as a donor of ADP-ribose moieties in ADP-ribosylation reactions and also as a precursor of the second messenger molecule cyclic ADP-ribose. β-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleot ide also acts as a substrate for bacterial DNA ligases and a group of enzymes called sirtuins that use NAD+ to remove acetyl groups from proteins. |
Relevant Products
-
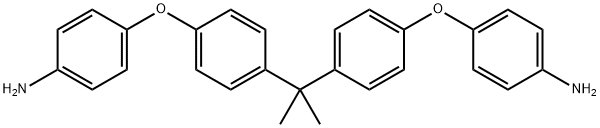
4,4-(4,4-Isopropylidenediphenyl-1,1-diyldioxy)dianiline
CAS:13080-86-9
-
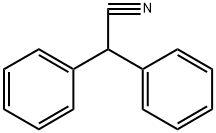
Diphenylacetonitrile
CAS:86-29-3