Product Details;
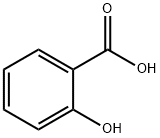
CasNo: 69-72-7
Molecular Formula: C7H6O3
Appearance: white crystalline powder
|
69-72-7 Name |
|
|
Name |
Salicylic acid |
|
Synonym |
2-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID;ACIDUM SALICYLICUM;ACETYLSALISYLIC ACID IMP C;ACETYLSALICYLIC ACID IMPURITY C;FEMA 3985;SALICYCLIC ACID;SALICYLIC ACID;RETARDER TSA |
|
69-72-7 Biological Activity |
|
|
Description |
Salicylic acid inhibits cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) activity independently of transcription factor (NF-κB) activation. |
|
Related Catalog |
Signaling Pathways >> Autophagy >> Autophagy Signaling Pathways >> Immunology/Inflammation >> COX Signaling Pathways >> Autophagy >> Mitophagy Research Areas >> Inflammation/Immunology Natural Products >> Phenols |
|
Target |
COX-2 Autophagy Mitophagy |
|
In Vivo |
In C57Bl/6 DIO mice, Salicylic acid decreases both fasting and postprandial plasma glucose levels. Furthermore, there is a trend to reduce plasma triglyceride levels after Salicylic acid treatment in C57Bl/6 DIO mice (P=0.059). Salicylic acid significantly reduces 11β-HSD1 mRNA in omental adipose tissue in C57Bl/6 DIO mice, with a similar trend in mesenteric adipose (P=0.057). In mesenteric adipose of C57Bl/6 DIO mice, Salicylic acid also reduces 11β-HSD1 enzyme activity[2]. |
|
References |
[1]. Mitchell JA, et al. Sodium salicylate inhibits cyclo-oxygenase-2 activity independently of transcription factor (nuclear factor kappaB) activation: role of arachidonic acid. Mol Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;51(6):907-12. [2]. Nixon M, et al. Salicylate downregulates 11β-HSD1 expression in adipose tissue in obese mice and in humans, mediating insulin sensitization. Diabetes. 2012 Apr;61(4):790-6. |
|
69-72-7 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
158-161 °C(lit.) |
|
Boiling point |
211 ºC (20 mmHg) |
|
Density |
1.44 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C7H6O3 |
|
Molecular Weight |
138.121 |
|
Flash Point |
157 ºC |
|
PSA |
57.53000 |
|
LogP |
2.06 |
|
Exact Mass |
138.031693 |
|
Vapour density |
4.8 (vs air) |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.616 |
|
Storage condition |
Store at RT. |
|
Water Solubility |
1.8 g/L (20 ºC) |
|
69-72-7 Description |
|
Salicylic acid (from Latin salix, willow tree, from the bark of which the substance used to be obtained) is a mono hydroxy benzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid and a beta hydroxy acid. This colorless crystalline organic acid is widely used in organic synthesis and functions as a plant hormone. It is derived from the metabolism of salicin. In addition to being an important active metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), which acts in part as a prod rug to salicylic acid, it is probably best known for its use in anti-acne treatments. The salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. |
|
69-72-7 Uses |
|
Salicylic acid is an FDA approved skin care ingredient used for the topical treatment of acne, and it's the only beta hydroxy acid (BHA) used in skin care products. Perfect for oily skin, salicylic acid is best known for its ability to deep clean excess oil out of pores and reduce oil production moving forward. Because salicylic acid keeps pores clean and unclogged, it prevents future whiteheads and blackheads from developing. Salicylic acid also exfoliates dead skin, and its anti-inflammatory properties make it a prime ingredient for those with psoriasis. Salicylic acid naturally occurs in willow bark, sweet birch bark, and wintergreen leaves, but synthetic versions are also used in skin care products. |
Relevant Products
-
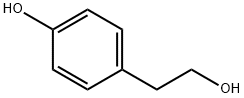
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
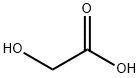
Glycolic acid
CAS:79-14-1
-
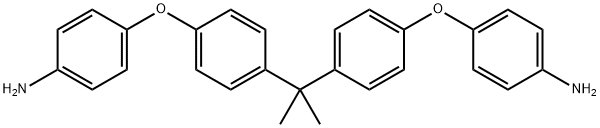
4,4-(4,4-Isopropylidenediphenyl-1,1-diyldioxy)dianiline
CAS:13080-86-9