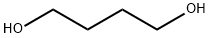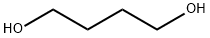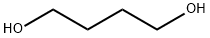
Product Details;
CasNo: 110-63-4
Molecular Formula: C4H10O2
Appearance: viscous colourless liquid
|
110-63-4 Name |
|
|
Name |
1,4-Butanediol |
|
Synonym |
1,4-Butandiol ,1,4-Butanediol ,Dabco BDO ,MFCD00002968 ,EINECS 203-786-5 ,Diol 14B,BDO,butane-1,4-diol,agrisynthb1d,1,4-Dihydroxybutane,1,4-Butylene Glycol,Butanediol,1,4-BD,sucolb,4-hydroxybutanol,Tetramethylene Glycol, 1,4-Butylene glycol,Tetramethylene glycol |
|
110-63-4 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
20 °C |
|
Boiling point |
228.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C4H10O2 |
|
Molecular Weight |
90.121 |
|
storage temp. |
Store below +30°C. |
|
Form and Color |
Liquid,Clear colorless |
|
Flash Point |
105.9±13.0 °C |
|
Exact Mass |
90.068077 |
|
PSA |
40.46000 |
|
LogP |
-1.02 |
|
Vapour density |
3.1 (vs air) |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.441 |
|
Stability |
Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, mineral acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides. |
|
Water Solubility |
Miscible |
|
110-63-4 Description |
|
1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD) is a colorless, viscous liquid derived from butane by placement of alcohol groups at each end of its molecular chain and is one of four stable isomers of butanediol.the hydroxyl function of each end group of the Butanediol reacts with different mono- and bifunctional reagents: for example with dicarboxylic acids to polyesters, with diisocyanates to polyurethanes, or with phosgene to polycarbonates. 1.4-Butanediol (BDO) is a high-quality intermediate. BDO and its derivatives are widely used for producing plastics, solvents, electronic chemicals and elastic fibers. Additionally BDO is also a building block for the synthesis of polyesterpolyols and polyetherpolyols. |
|
110-63-4 Uses |
|
|
110-63-4 Reactivity Profile |
|
1,4-Butanediol is heat and light sensitive. 1,4-Butanediol reacts with acid chlorides, acid anhydrides and chloroformates; reacts with oxidizing agents and reducing agents. 1,4-Butanediol is incompatible with isocyanates and acids; also incompatible with peroxides, perchloric acid, sulfuric acid, hypochlorous acid, nitric acid, caustics, acetaldehyde, nitrogen peroxide and chlorine. |
|
110-63-4 Safety Profile |
|
A human poison by an unspecified route. Moderately toxic byingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects: altered sleep time. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, mist, foam, CO2, dry chemical. Incompatible with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes. |
Relevant Products
-
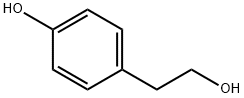
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
1,4-Butanediol
CAS:110-63-4
-
1,4-Butanediol
CAS:110-63-4