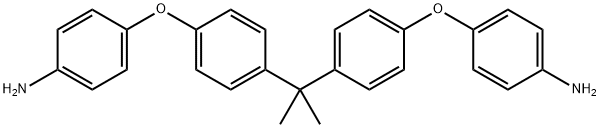
13080-86-9
- Product Name:Benzenamine,4,4'-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(4,1-phenyleneoxy)]bis-
- Molecular Formula:C27H26N2O2
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 13080-86-9
Molecular Formula: C27H26N2O2
13080-86-9 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C27H26N2O2
- Molecular Weight:410.516
- Melting Point:127-130 °C
- Boiling Point:587.1 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:5.16±0.10(Predicted)
- Flash Point:322.8 °C
- PSA:70.50000
- Density:1.178 g/cm3
- LogP:7.92390
13080-86-9 Usage
Chemical Properties
4,4'-(4,4'-Isopropylidenediphenyl-1,1'-diyldioxy)dianiline is white solid
Uses
It is applied in pharmaceutical industry.
Uses
4,4'-(4,4'-Isopropylidenediphenyl-1,1'-diyldioxy)dianiline is used for preparation polyimide and epoxy resin material.
13080-86-9 Relevant articles
Bis(azobenzene) diamines and photomechanical polymers made therefrom
-
, (2017/05/31)
Bis(azo-benzene) diamine monomers and a method of synthesizing the monomers are provided. The bis(azo-benzene) diamine monomers, in combination with amine reactive monomers, form polymers, such as polyimides and copolyimides, having photomechanical and thermomechanical properties.
Method for preparing 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl] propane
-
Paragraph 0026; 0027; 0030; 0031; 0035; 0037, (2017/08/28)
The invention belongs to the technical field of polyimide materials and epoxy curing agents and specifically discloses a method for preparing 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl] propane with low metal ion content. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out a synthetic reaction of nitride 2,2-bis[4-(4-nitrophenoxy)phenyl] propane on 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane, parachloronitrobenzene and anhydrous potassium carbonate in a system taking N,N-dimethyl formamide as a solvent and taking xylene as a dehydrating agent; taking absolute ethyl alcohol as a solvent, taking Ni-B/C as a catalyst, taking hydrazine hydrate as a reducing agent, and reducing the 2,2-bis[4-(4-nitrophenoxy)phenyl] propane into a target initial product 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl] propane; and finally, removing the metal ions by using a complex-precipitation method, thereby obtaining the target product. The method disclosed by the invention is low in production cost, high in product purity, low in metal ion content and high in yield, and the electronic grade monomer standard can be met.
Multivalent photo-crosslinkable coumarin-containing polybenzoxazines exhibiting enhanced thermal and hydrophobic surface properties
Lin, Ruey-Chorng,Mohamed, Mohamed Gamal,Hsu, Kuo-Chih,Wu, Jia-Yu,Jheng, Yu-Ru,Kuo, Shiao-Wei
, p. 10683 - 10696 (2016/02/09)
In this study, mono-, bi-, and trivalent coumarin-containing benzoxazine monomers (mono-, di-, and tri-coumarin BZ) were synthesized in high yield and purity by facile Mannich reactions of 4-methyl-7-hydroxycoumarin and paraformaldehyde with aniline, bisphenol A-NH2, and 1,3,5-tri(4-aminobenzene), respectively, in 1,4-dioxane. 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and high resolution mass spectroscopy support the chemical structures of these three benzoxazine monomers. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and FTIR spectroscopy were used to investigate the curing polymerization behavior and photodimerization ([2π + 2π] cycloaddition) of the coumarin units of mono-, di-, and tri-coumarin BZ to form poly(mono-coumarin BZ), poly(di-coumarin BZ), and poly(tri-coumarin BZ), respectively. DSC measurement revealed that the thermal polymerization temperature of coumarin-containing benzoxazine monomers was lower than that of the model compound 3-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-benzooxazine (263°C) which was attributed to the catalytic effect of the coumarin moiety and a strong electron withdrawing electron conjugated CC bond in the coumarin unit. In addition, the glass transition and thermal decomposition temperatures of poly(tri-coumarin BZ) (Tg = 240°C; Td5 = 370°C) were higher than poly(di-coumarin BZ) and poly(mono-coumarin BZ), consistent with the former's higher crosslinking density. In addition, the water contact angles of poly(tri-coumarin BZ) polymers prepared with and without photo-dimerization prior to thermal curing (112 and 110°, respectively) were higher than the corresponding poly(mono-coumarin BZ) and poly(di-coumarin BZ), presumably because of greater degrees of intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the CO units of the coumarin moieties and the phenolic OH units of the benzoxazine rings, resulting in lower surface free energies. Thus, the presence of multivalent photo-crosslinkable coumarin units enhanced the thermal and hydrophobic surface properties of these polybenzoxazines.
Impact of backbone rigidity on the photomechanical response of glassy, azobenzene-functionalized polyimides
Wang, David H.,Wie, Jeong Jae,Lee, Kyung Min,White, Timothy J.,Tan, Loon-Seng
, p. 659 - 667 (2014/02/14)
Azobenzene-functionalized polyimide materials can directly transduce light into mechanical force. Here, we examine the impact of polymer backbone rigidity on the photomechanical response in a series of linear, azobenzene-functionalized polymers. The rigidity of the backbone was varied by the polymerization of five dianhydride monomers with a newly synthesized diamine (azoBPA-diamine). The azobenzene-functionalized linear polymers exhibit glass transition temperatures (Tg) ranging from 276 to 307 C and maintain excellent thermal stability. The photomechanical response of these materials was characterized by photoinduced cantilever bending as well as direct measurement of photogenerated stress upon exposure to linearly polarized, 445 nm light. Increasing the rigidity of the polymer backbone increases the magnitude of stress that is generated but decreases the angle of cantilever deflection.
13080-86-9 Process route
-
![2,2-bis[4-(4-nitrophenoxy)phenyl]propane](/upload/2023/1/2e274f4a-aa49-43a3-9d30-dab350b68662.png)
- 20653-11-6
2,2-bis[4-(4-nitrophenoxy)phenyl]propane

-

- 7803-57-8,79785-97-0
hydrazine hydrate

-

- 13080-86-9,158066-25-2
2,2-bis-{4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl}propane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2,2-bis[4-(4-nitrophenoxy)phenyl]propane; With palladium 10% on activated carbon; In ethanol; at 50 ℃; Reflux;
hydrazine hydrate; In ethanol; at 80 - 90 ℃; for 3h;
|
85% |
-

- 80-05-7
BPA

-

- 13080-86-9,158066-25-2
2,2-bis-{4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl}propane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1: Na2CO3
2: Zn, AcOH
With sodium carbonate; acetic acid; zinc;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1: potassium carbonate; N,N-dimethyl-formamide / 12 h / Reflux
2: palladium 10% on activated carbon; hydrazine / ethanol; water / 12.5 h / 85 °C / Reflux
With palladium 10% on activated carbon; potassium carbonate; N,N-dimethyl-formamide; hydrazine; In ethanol; water;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1: potassium carbonate / N,N-dimethyl-formamide / 24 h / 20 °C
2: palladium on activated charcoal; hydrogen / ethyl acetate / 24 h / 20 °C / 2844.39 Torr
With palladium on activated charcoal; hydrogen; potassium carbonate; In ethyl acetate; N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1.1: potassium carbonate / N,N-dimethyl-formamide / 48 h / 130 °C / Inert atmosphere
2.1: palladium 10% on activated carbon / ethanol / 2 h / 80 - 90 °C / Inert atmosphere
2.2: 48 h / Reflux
With palladium 10% on activated carbon; potassium carbonate; In ethanol; N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 2 steps
1: potassium carbonate / N,N-dimethyl-formamide / 24 h / 20 °C / Inert atmosphere
2: palladium on activated charcoal; hydrogen / ethyl acetate / 24 h / 20 °C / 2844.39 Torr
With palladium on activated charcoal; hydrogen; potassium carbonate; In ethyl acetate; N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
|
13080-86-9 Upstream products
-
20653-11-6

2,2-bis[4-(4-nitrophenoxy)phenyl]propane
-
80-05-7

BPA
-
100-00-5

4-chlorobenzonitrile
-
350-46-9

4-Fluoronitrobenzene
13080-86-9 Downstream products
-
1166187-87-6

P-BAPP-HB
-
1190053-16-7

BAA
-
79922-55-7

2,2'-bis-[4-(4-maleimidephenoxy)phenyl]propane
-
1333382-36-7

C49H36N4O8
Relevant Products
-
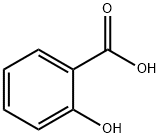
Salicylic acid
CAS:69-72-7
-
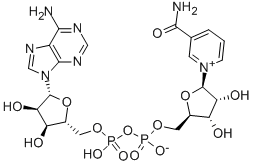
beta-Diphosphopyridine nucleotide
CAS:53-84-9