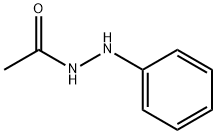
114-83-0
- Product Name:1-Acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine
- Molecular Formula:C8H10N2O
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 114-83-0
Molecular Formula: C8H10N2O
Appearance: colorless prisms or white solid
114-83-0 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C8H10N2O
- Molecular Weight:150.18
- Appearance/Colour:colorless prisms or white solid
- Vapor Pressure:1E-06mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:128-131 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.6180 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:214.1 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:12.75±0.23(Predicted)
- Flash Point:87.8 °C
- PSA:41.13000
- Density:1.143 g/cm3
- LogP:1.61350
114-83-0 Usage
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
Uses
1-Acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine is an Anaerobically curable compound.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 30, p. 2486, 1965 DOI: 10.1021/jo01018a525
General Description
Colorless prisms or white solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Water insoluble.
Reactivity Profile
1-Acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine is an amide and an amine. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition 1-Acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine emits toxic fumes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 1-Acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine are not available. 1-Acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine is probably combustible.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the hydrazine from aqueous EtOH. [Beilstein 15 H 241.]
InChI:InChI=1/C6H8N2.C2H4O2/c7-8-6-4-2-1-3-5-6;1-2(3)4/h1-5,8H,7H2;1H3,(H,3,4)
114-83-0 Relevant articles
A formal [3+2] cycloaddition reaction of: N -methylimidazole as a masked hydrogen cyanide: Access to 1,3-disubstitued-1 H -1,2,4-triazoles
Yavari, Issa,Khaledian, Omid
supporting information, p. 9150 - 9153 (2020/10/02)
N-Methylimidazole (NMI) can act as a masked HCN in the synthesis of 1,3-disubstitued-1H-1,2,4-triazoles via a formal cycloaddition reaction of hydrazonoyl chloride with NMI. The product was proved to be formed via an initial nucleophilic substitution of hydrazonoyl chloride with NMI following cyclization and two sequential C-N bond cleavages. This journal is
Synthesis of acetamides via oxidative C–C bond cleavage of ketones catalyzed by Cu-immobilized magnetic nanoparticles
Yazdani, Elahe,Pazoki, Farzane,Salamatmanesh, Arefe,Nejad, Masoume Jadidi,Miraki, Maryam Kazemi,Heydari, Akbar
, (2020/07/27)
Copper supported on magnetite nanoparticles modified with environmentally friendly ligand tricine was devised for synthesis of acetamides via C–C oxidative cleavage of ketones with amines. The catalyst was characterized using different techniques, including Fourier transform infrared, X-ray diffraction, scannin electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, thermogravimetric analysis, and energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy. The protocol showed relatively high yields of acetamide products. Furthermore, the magnetic recovery of the catalyst rendered the overall process fast and efficient. It was used in the reaction for six consecutive cycles with negligible loss of catalytic activity. This research is the first report of application of magnetic nanocatalysts for synthesis of acetamides from ketones of low activity through a C–C bond cleavage strategy.
The impact of cation structure upon the acidity of triazolium salts in dimethyl sulfoxide
Konstandaras, Nicholas,Dunn, Michelle H.,Guerry, Max S.,Barnett, Christopher D.,Cole, Marcus L.,Harper, Jason B.
supporting information, p. 66 - 75 (2019/12/26)
A series of triazolium salts, selected for their varying electronic and steric properties, were prepared and their pKa values were determined in DMSO at 25 °C using the bracketing indicator method. The effect of each systematic structural variation upon the acidity of the triazolium cation has been considered, in particular examining the effects of systematically altering electronic properties, quantified through the use of Hammett σ parameters. The first pKa value for an azolium salt that generates a mesionic carbene is also reported. These new data allow for the selection of appropriate bases for the deprotonation of such triazolium salts and the potential to correlate the pKa values determined herein with the nucleophilicity of the corresponding carbenes.
A magnetically recoverable copper–salen complex as a nano-catalytic system for amine protection via acetylation using thioacetic acid
Yazdani, Elahe,Kazemi Miraki, Maryam,Salamatmanesh, Arefe,Azarnia, Jamshid,Azizi, Kobra,Ghandi, Leila,Heydari, Akbar
, p. 1775 - 1793 (2019/01/16)
A novel copper(II)–salen complex was immobilized on the surface of magnetite nanoparticles using chitosan as a linker. This system exhibits superior catalytic activity in acetyl protection of various amines with thioacetic acid as the acetylating reagent. The method has advantages over others in high selectivity, simple work-up, green reaction medium and the application of an easily recoverable heterogeneous catalyst.
114-83-0 Process route
-

- 61053-62-1
2-methanesulfonyl-acetoacetic acid ethyl ester

-

- 100-63-0
phenylhydrazine

-

- 4455-15-6
ethyl methanesulfonylacetate

-

- 114-83-0
1-acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
-

- 2684-02-8
benzenediazonium

-

- 579-07-7
1-Phenylpropane-1,2-dione

-

- 20999-77-3
1-phenyl-propane-1,2-dione-2-phenylhydrazone

-

- 114-83-0
1-acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine

-

- 532-96-7
N-benzoyl-N'-phenylhydrazine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With titanium(III) chloride; In acetic acid; at 50 ℃; for 0.666667h;
|
40% 29% 25% |
114-83-0 Upstream products
-
28286-72-8

acetyl-methyl-malonic acid diethyl ester
-
72358-76-0

phenylhydrazine acetate
-
20604-81-3

(1-nitro-ethylidene)-phenyl-hydrazine
-
108-24-7

acetic anhydride
114-83-0 Downstream products
-
38604-74-9

N'-acetyl-N'-phenylacetohydrazide
-
73006-31-2

phthalic acid mono-(N'-acetyl-N-phenyl-hydrazide)
-
14575-62-3

5-methyl-1-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-pyrazol-3-one
-
19735-89-8

3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazolin-5(4H)-one
Relevant Products
-
Melanotan II
CAS:121062-08-6