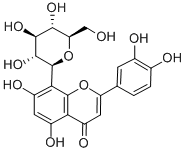
28608-75-5
- Product Name:4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one,2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-8-b-D-glucopyranosyl-5,7-dihydroxy-
- Molecular Formula:C21H20O11
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 28608-75-5
Molecular Formula: C21H20O11
Appearance: yellow powder
28608-75-5 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C21H20O11
- Molecular Weight:448.383
- Appearance/Colour:yellow powder
- Vapor Pressure:3.63E-28mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:260-285 °C
- Refractive Index:1.767
- Boiling Point:816.1 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:6.24±0.40(Predicted)
- Flash Point:289.1 °C
- PSA:201.28000
- Density:1.759 g/cm3
- LogP:-0.20270
28608-75-5 Usage
Description
Orientin is a flavone glycoside originally isolated from P. orientale that has diverse biological activities, including antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Orientin scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH; ) radicals with an IC50 value of 316.21 μg/ml. It also decreases the cytopathic effects of parainfluenza type 3 virus with an IC50 value of 11.7 μg/ml and a cytotoxic concentration (CC50) value of 375 μg/ml in Hep-2 cells. Orientin (5-40 μM) inhibits LPS-induced barrier disruption, decreases the expression of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), phosphorylated p38, and NF-κB, and decreases TNF-α production and IL-6 secretion in a dose-dependent manner in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). It also prolongs survival in a mouse model of LPS-induced lethal endotoxemia when administered at a dose of 36 μg/animal 12 hours after LPS administration.
Chemical Properties
Yellow powder
Uses
Orientin is a flavone, a chemical flavonoid compound. Orientin have been investigated for its anti-oxidant, antihypertensive and antihyperlipidemic effects.
Definition
ChEBI: A C-glycosyl compound that is luteolin substituted by a beta-D-glucopyranosyl moiety at position 8.
InChI:InChI=1/C21H20O11/c22-6-14-17(28)18(29)19(30)21(32-14)16-11(26)4-10(25)15-12(27)5-13(31-20(15)16)7-1-2-8(23)9(24)3-7/h1-5,14,17-19,21-26,28-30H,6H2/t14-,17-,18+,19-,21+/m1/s1
28608-75-5 Relevant articles
C-Glycosylflavones with acetyl substitution from Rumex acetosa L.
Kato,Morita
, p. 2277 - 2280 (1990)
-
-
Seikel,Bushnell
, p. 1995 (1959)
-
Efficient Production of Orientin and Vitexin from Luteolin and Apigenin Using Coupled Catalysis of Glycosyltransferase and Sucrose Synthase
Liu, Shike,Lyu, Yunbin,Yu, Shiqin,Cheng, Jie,Zhou, Jingwen
, p. 6578 - 6587 (2021/06/28)
Orientin and vitexin are flavone 8-C-glycosides that exhibit many biological characteristics. This study aimed to establish a two-enzyme-coupled catalytic strategy to enhance the biosynthesis of orientin and vitexin from apigenin and luteolin, respectively. The C-glucosyltransferase (TcCGT1) gene from Trollius chinensis was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). The optimal activity of TcCGT1 was achieved at pH 9.0 and 37 °C. TcCGT1 was relatively stable over the pH range of 7.0-10.0 at a temperature lower than 45 °C. The coupled catalytic strategy of TcCGT1 and different sucrose synthases was adopted to enhance the production of orientin and vitexin. By optimizing the coupling reaction conditions, orientin and vitexin production successfully achieved 2324.4 and 5524.1 mg/L with a yield of 91.4 and 89.3% (mol/mol), respectively. The coupled catalytic strategy proposed in this study might serve as a promising candidate for the large-scale production of orientin and vitexin in the future.
Molecular and Structural Characterization of a Promiscuous C-Glycosyltransferase from Trollius chinensis
He, Jun-Bin,Zhao, Peng,Hu, Zhi-Min,Liu, Shuang,Kuang, Yi,Zhang, Meng,Li, Bin,Yun, Cai-Hong,Qiao, Xue,Ye, Min
supporting information, p. 11513 - 11520 (2019/07/16)
Herein, the catalytic promiscuity of TcCGT1, a new C-glycosyltransferase (CGT) from the medicinal plant Trollius chinensis is explored. TcCGT1 could efficiently and regio-specifically catalyze the 8-C-glycosylation of 36 flavones and other flavonoids and could also catalyze the O-glycosylation of diverse phenolics. The crystal structure of TcCGT1 in complex with uridine diphosphate was determined at 1.85 ? resolution. Molecular docking revealed a new model for the catalytic mechanism of TcCGT1, which is initiated by the spontaneous deprotonation of the substrate. The spacious binding pocket explains the substrate promiscuity, and the binding pose of the substrate determines C- or O-glycosylation activity. Site-directed mutagenesis at two residues (I94E and G284K) switched C- to O-glycosylation. TcCGT1 is the first plant CGT with a crystal structure and the first flavone 8-C-glycosyltransferase described. This provides a basis for designing efficient glycosylation biocatalysts.
Biosynthesis of natural and novel C-glycosylflavones utilising recombinant Oryza sativa C-glycosyltransferase (OsCGT) and Desmodium incanum root proteins
Hao,Caulfield,Hamilton,Pickett,Midega,Khan,Wang,Hooper
, p. 73 - 87 (2016/04/06)
The rice C-glycosyltransferase (OsCGT) is one of only a small number of characterised plant C-glycosyltransferases (CGT) known. The enzyme C-glucosylates a 2-hydroxyflavanone substrate with UDP-glucose as the sugar donor to produce C-glucosyl-2-hydroxyflavanones. We tested substrate specificity of the enzyme, using synthetic 2-hydroxyflavanones, and showed it has the potential to generate known natural CGFs that have been isolated from rice and also other plants. In addition, we synthesised novel, unnatural 2-hydroxyflavanone substrates to test the B-ring chemical space of substrate accepted by the OsCGT and demonstrated the OsCGT capacity as a synthetic reagent to generate significant quantities of known and novel CGFs. Many B-ring analogues are tolerated within a confined steric limit. Finally the OsCGT was used to generate novel mono-C-glucosyl-2-hydroxyflavanones as putative biosynthetic intermediates to examine the potential of Desmodium incanum biosynthetic CGTs to produce novel di-C-glycosylflavones, compounds implicated in the allelopathic biological activity of Desmodium against parasitic weeds from the Striga genus.
Flavone C-glycosides from the flowers of Trollius chinensis and their anti-complementary activity
Liu, Jiang-Yun,Li, Sheng-Yin,Feng, Jian-Yong,Sun, Yan,Cai, Jin-Na,Sun, Xiao-Fei,Yang, Shi-Lin
, p. 325 - 331 (2013/06/27)
Phytochemical investigation of ethanol extract from the flowers of Trollius chinensis Bunge resulted in the isolation of two new flavone C-glycosides (1-2), along with 10 known compounds (3-12). The structures of the new compounds were established as 6?-(
28608-75-5 Process route
-

-
C15H12O7

-

-
UDP-glucose

-

- 4261-42-1
isoorientin

-

- 7480-94-6,28608-75-5
Luteolin-8-C-glucoside
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With recombinant Oryza sativa C-glycosyltransferase; In ethanol; at 30 ℃; pH=7.5; Enzymatic reaction;
|
56% 43% |
-

- 381686-07-3
2-(3,4-bis-benzyloxyphenyl)-7-benzyloxy-8-C-(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-benzyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-5-hydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one

-

- 7480-94-6,28608-75-5
Luteolin-8-C-glucoside
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogen; palladium on activated charcoal; In ethanol; ethyl acetate; at 20 ℃;
|
100% |
28608-75-5 Upstream products
-
4261-42-1

3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxy-6-C-glucopyranosylflavone
-
131507-99-8

2″,6″-O-diacetylorientin
-
381686-07-3

2-(3,4-bis-benzyloxyphenyl)-7-benzyloxy-8-C-(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-benzyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-5-hydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
-
39548-86-2

1‐(2‐(benzyloxy)‐4,6‐dihydroxyphenyl)ethan‐1‐one
28608-75-5 Downstream products
-
4261-42-1

3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxy-6-C-glucopyranosylflavone
-
50-99-7

D-glucose
-
4261-42-1

isoorientin
-
1377947-82-4

orientin-2-O-β-D-galactopyranoside
Relevant Products
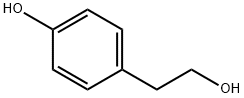
-
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
Thymosin beta 4 acetate
CAS:77591-33-4
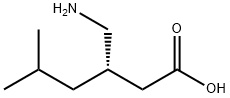
-
Pregabalin
CAS:148553-50-8