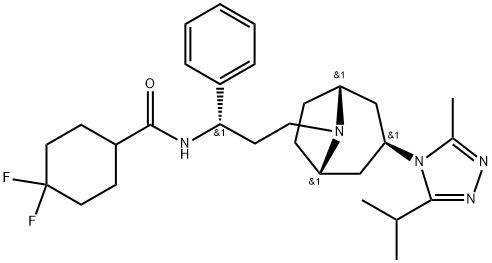
376348-65-1
- Product Name:Maraviroc
- Molecular Formula:C29H41F2N5O
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details;
CasNo: 376348-65-1
Molecular Formula: C29H41F2N5O
Appearance: Brown solid
376348-65-1 Properties
- Molecular Formula:C29H41F2N5O
- Molecular Weight:513.674
- Appearance/Colour:Brown solid
- Melting Point:79-81 °C
- Refractive Index:1.627
- PKA:7.3(at 25℃)
- PSA:63.05000
- Density:1.29 g/cm3
- LogP:6.27970
376348-65-1 Usage
Description
Maraviroc is the first CCR5 receptor antagonist that has been developed and launched for the treatment of HIV-1. Maraviroc binds in a slowly reversible, allosteric manner to CCR5, which is one of two principle chemokine co-receptors for viral entry into the host cell, the other being CXCR4. Binding of maraviroc to CCR5 induces conformational changes within the chemokine receptor, thereby preventing CCR5 binding to the viral gp120 protein and the ultimate CCR5- mediated virus-cell fusion that is a prerequisite for HIV invasion. Maraviroc, with its unique mechanism of action as a fusion inhibitor, joins the greater than 20 marketed antiretrovirals, including nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), and PIs. It is approved for use in combination with these other antiretroviral drugs in adult patients with R5-tropic HIV-1 infection (but not X4 or dual/mixed tropic HIV-1).
Chemical Properties
Brown Solid
Originator
Pfizer (US)
Uses
Maraviroc is a potent, non-competitive CCR5 receptor antagonist; inhibits binding of HIV viral coat protein gp120. Antiviral.
Uses
Potent, non-competitive CCR5 receptor antagonist; inhibits binding of HIV viral coat protein gp120. Antiviral
Uses
Maraviroc is a CCR5 antagonist for MIP-1α, MIP-1β and RANTES with IC50 of 3.3 nM, 7.2 nM and 5.2 nM, respectively
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4,4-difluorocyclohexanecarboxylic acid and the primary amino group of (1S)-3-[(3-exo)-3-(3-isopropyl-5-methyl-4H-1,2,4- riazol-4-yl)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-8-yl]-1-phenylpropylamine. An antiretroviral drug, it prevents the interaction of HIV-1 gp120 and chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) necessary for CCR5-tropic HIV-1 to enter cells.
Brand name
Selzentry
Acquired resistance
In most patients (c. 60%) failure of response is associated with the selection of virus that can use CXCR4 as its entry co-receptor. Evidence for the selection of virus that continues to use CCR5 has also been described.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A spirodiketopiperazine formulated as tablets for oral use.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Maraviroc is metabolised by cytochrome P450 3A4. The transport and absorption of maraviroc in the intestine and bile is regulated by P-glycoprotein (Pgp). Maraviroc binds to the active site pocket of chemokine receptor CCR5 making the receptor inactive.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 33% (300 mg dose) Cmax 150 mg twice daily: c. 332 μg/L* Cmin 150 mg twice daily: c. 101 μg/L* Plasma half-life: c. 13.2 h (30 mg iv administration) Volume of distribution: c. 194 L Plasma protein binding: c. 76% Absorption The absolute bioavailability of a 100 mg dose is 23% and is predicted to be 33% after a 300 mg dose. Co-administration of a 300 mg tablet and a high-fat meal has resulted in reduced Cmax and AUC by 33% in healthy volunteers. However, because no food restrictions were enacted during clinical trials, maraviroc may be taken with or without food. Distribution Animal experiments suggest low CSF concentrations around 10% of free plasma concentrations. It is not known whether it passes into breast milk. A study of genital tract secretions and vaginal tissue in healthy HIV-uninfected female volunteers suggest a concentration in cervicovaginal fluid more than four-fold higher than that in plasma. Metabolism It is a substrate for CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein, but does not appear to inhibit or induce CYP3A4. Excretion Seventy-six and 19% of a radiolabeled maraviroc dose were recovered in the feces and urine, respectively.
Clinical Use
Treatment of HIV infection (in combination with other antiretroviral drugs) in treatment-experienced patients On November 20, 2009, the US Food and Drug Administration approved a supplemental new drug application to expand the indication for maraviroc to include combination antiretroviral treatment of treatmentnaive adults infected with CCR5-tropic HIV virus
Side effects
There has been some concern that CCR5 blockade may result in decreased immune surveillance and a subsequent increased risk of development of malignancies (e.g. lymphomas). Genetic deficiency of the CCR5 co-receptor is also known to be a risk factor for the development of symptomatic West Nile virus infection. No evidence for an increase in either of these potential risks has so far emerged. The toxicity profile appears relatively benign. The most common adverse events described so far include diarrhea, fatigue, headache and nausea. In placebo-controlled studies the only differences to emerge were fever (6% versus 4% in the placebo group) and headache (2% versus 6% with placebo). Discontinuation because of adverse events was uncommon and the same in both groups.
Side effects
Overall, maraviroc was well tolerated with the most common adverse events being cough, fever, colds, rash, muscle and joint pain, stomach pain, and dizziness. While some patients did experience liver enzyme elevation, these events did not appear to be doserelated. Since hepatotoxicity did occur in one patient with prior liver function abnormalities, maraviroc s label warns of a potentially increased risk of hepatoxicity with treatment. Postural hypotension was also observed in a dosedependent manner; however, no patients discontinued therapy as a result. As a substrate for CYP3A4, the dose of maraviroc should be reduced by 50% in the presence of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Conversely, concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers requires a 50% increase in maraviroc dose. While there are no contraindications, maraviroc should be used with caution in patients with liver dysfunction, high risk of cardiovascular events, and pre-existing postural hypotension.
Synthesis
The synthesis of maraviroc involves the convergent connection of a triazole-substituted tropane moiety, a phenylpropyl fragment with a benzylic chiral center, and a 4,4-difluorocyclohexyl unit. In the presence of aqueous HCl and sodium acetate, 2,5-dimethoxytetrahydrofuran is cyclized with benzylamine and 2-oxomalonic acid to afford 8-benzyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-one. The ketone is converted to an amine via reduction of an intermediate oxime. Carbodiimide-mediated coupling of this amine with isobutyric acid yields the isobutyramide that is subsequently cyclized to the 1,2,4-triazole with acetic hydrazide. The benzyl-protected amine is then liberated by transfer hydrogenation (ammonium formate and palladium hydroxide) and subjected to reductive amination with 3(S)-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)-3-phenylpropionaldehyde by means of sodium triacetoxyborohydride. Removal of the BOC-protecting group establishes the handle for the final amide coupling with 4,4-difluorocyclohexane carboxylic acid to provide maraviroc.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased by clarithromycin and telithromycin, consider reducing dose of maraviroc; concentration reduced by rifampicin, consider increasing dose of maraviroc. Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by St John’s wort - avoid. Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole. Antivirals: concentration increased by atazanavir, cobicistat, darunavir, indinavir, lopinavir and saquinavir - consider reducing maraviroc dose; concentration reduced by efavirenz - consider increasing dose of maraviroc; concentration of fosamprenavir reduced - avoid. Orlistat: absorption possibly reduced by orlistat.
References
1) Dorr?et al.?(2005),?Maraviroc (UK-427,857), a Potent, Orally Bioavailable, and Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Chemokine Receptor CCR5 with Broad-Spectrum Anti-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Activity;?Antimicrob.Agents Chemother.?49?4721 2) Velasco-Velazquez?et al.?(2012),?CCR5 antagonist blocks metastasis of basal breast cancer cells;?Cancer Res.?72?3839 3) Singh?et al.?(2018),?CCR5/CCL5 axis interaction promotes migratory and invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells;?Sci.Rep.?8?1323 4) Pervaiz?et al.?(2015),?CCR5 blockage by maraviroc induces cytotoxic and apoptotic effects in colorectal cancer cells;?Med.Oncol.?32?158 5) Halvorsen?et al.?(2016),?Maraviroc decreases CCL8-mediated migration of CCR5(+) regulatory T cells and reduces metastatic tumor growth in the lungs;?Oncoimmunology?5?e1150398 6) Zi?et al.?(2017),?Treatment with the C-C chemokine receptor type 5(CCR5)-inhibitor maraviroc suppresses growth and induces apoptosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells;?Am.J.Cancer Res.?7?869 7) Halama?et al.?(2016),?Tumoral Immune Cell Exploitation in Colorectal Cancer Metastases Can Be targeted Effectively by Anti-CCR5 Therapy in Cancer Patients;?Cancer Cell?29?587
InChI:InChI=1/C29H41F2N5O/c1-19(2)27-34-33-20(3)36(27)25-17-23-9-10-24(18-25)35(23)16-13-26(21-7-5-4-6-8-21)32-28(37)22-11-14-29(30,31)15-12-22/h4-8,19,22-26H,9-18H2,1-3H3,(H,32,37)/t23-,24+,25?,26-/m0/s1
376348-65-1 Relevant articles
Preparation method of
-
Paragraph 0070; 0087-0093; 0110-0116; 0133-0138, (2021/10/27)
The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking a halogen-containing azide compound as a raw material in γ-position, carrying out a reaction, and preparing and a derivative thereof. The method is characterized in γ-position halogen-containing azide compound as a raw material and is subjected to reduction. A series of non-sequential reactions, such as hydrolysis, substitution, condensation, reductive amination, and the like. A target compound, that is, a Mahalanobis derivative, can be obtained. The preparation method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost, less side reaction, high product purity, simplicity and convenience in separation and purification and the like. The invention further provides the pulvernolol and derivatives thereof prepared by the method and application thereof.
A practical catalytic reductive amination of carboxylic acids
Andrews, Keith G.,Denton, Ross M.,Hirst, David J.,Stoll, Emma L.,Tongue, Thomas,Valette, Damien
, p. 9494 - 9500 (2020/10/02)
We report reductive alkylation reactions of amines using carboxylic acids as nominal electrophiles. The two-step reaction exploits the dual reactivity of phenylsilane and involves a silane-mediated amidation followed by a Zn(OAc)2-catalyzed amide reduction. The reaction is applicable to a wide range of amines and carboxylic acids and has been demonstrated on a large scale (305 mmol of amine). The rate differential between the reduction of tertiary and secondary amide intermediates is exemplified in a convergent synthesis of the antiretroviral medicine maraviroc. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that a residual 0.5 equivalents of carboxylic acid from the amidation step is responsible for the generation of silane reductants with augmented reactivity, which allow secondary amides, previously unreactive in zinc/phenylsilane systems, to be reduced.
METHOD FOR PREPARING MARAVIROC
-
Paragraph 0030, (2019/08/26)
Provided is a method for preparing a tropane derivative, maraviroc, including reacting a compound of formula (II) with a compound of formula (I), wherein the compound of formula (II) is prepared by the steps of acetylation of a compound of formula (III), activation and substitution of a compound of formula (IV) by a chlorination agent, cyclization of a compound of formula (V), and debenzylation of a compound of formula (VI) by hydrogenation. Hence, the present disclosure provides a method for preparing maraviroc with good yield and simple operation.
Asymmetric Mannich Reaction and Construction of Axially Chiral Sulfone-Containing Styrenes in One Pot from α-Amido Sulfones Based on the Waste-Reuse Strategy
Li, Dongmei,Tan, Yu,Peng, Lei,Li, Shan,Zhang, Nan,Liu, Yidong,Yan, Hailong
supporting information, p. 4959 - 4963 (2018/08/24)
A simultaneous asymmetric Mannich reaction and the construction of axially chiral sulfone-containing styrenes in one pot from α-amido sulfones based on the waste-reuse strategy was demonstrated. A series of chiral β-amino diesters and axially chiral sulfone-containing styrenes with various functional groups were synthesized in good to excellent yields and enantioselectivities under mild conditions. In addition, this protocol has been successfully applied to synthesize the anti-HIV drug Maraviroc and chiral trichloro derivatives.
376348-65-1 Process route
-

- 423165-07-5
UK-408027

-

- 376348-78-6
4,4-difluorocyclohexanecarboxylic acid (3-oxo-1-phenyl-propyl)-amide

-

- 376348-65-1,674782-29-7
maraviroc
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
UK-408027; 4,4-difluorocyclohexanecarboxylic acid (3-oxo-1-phenyl-propyl)-amide; With acetic acid; In 1,2-dichloro-ethane; at 20 ℃; for 12h;
With sodium tris(acetoxy)borohydride; In 1,2-dichloro-ethane; at 20 ℃; for 12h; Further stages.;
|
|
|
UK-408027; 4,4-difluorocyclohexanecarboxylic acid (3-oxo-1-phenyl-propyl)-amide; In tetrahydrofuran; for 0.166667h; Cooling with ice;
With acetic acid; In tetrahydrofuran; for 0.166667h;
With sodium tris(acetoxy)borohydride; In tetrahydrofuran;
|
4.6 g |
|
With sodium tris(acetoxy)borohydride; acetic acid; In 1,2-dichloro-ethane; at 0 ℃; for 3h; Inert atmosphere;
|
-
![(S)-3-((1R,3R,5S)-3-(3-isopropyl-5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)-1-phenylpropan-1-amine](/upload/2023/1/07908915-3af1-44a1-b1a1-57893038057b.png)
- 376348-71-9
(S)-3-((1R,3R,5S)-3-(3-isopropyl-5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)-1-phenylpropan-1-amine

-

- 376348-75-3
4,4-difluorocyclohexane-1-carbonyl chloride

-

- 376348-65-1,674782-29-7
maraviroc
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With sodium carbonate; In dichloromethane; water; at 0 - 20 ℃;
|
82% |
|
With sodium carbonate; In dichloromethane; water; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 0.5h;
|
59% |
376348-65-1 Upstream products
-
122665-97-8

4,4-difluorocyclohexanecarboxylic acid
-
376348-71-9

(S)-3-((1R,3R,5S)-3-(3-isopropyl-5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)-1-phenylpropan-1-amine
-
178312-47-5

ethyl 4,4-difluorocyclohexane-1-carboxylate
-
376348-70-8

tert-butyl (1S)-3-[3-(3-isopropyl-5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-exo-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-8-yl]-1-phenylpropylcarbamate
Relevant Products
-
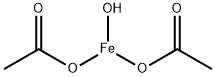
ferric acetate
CAS:10450-55-2
-
Thymosin beta 4 acetate
CAS:77591-33-4